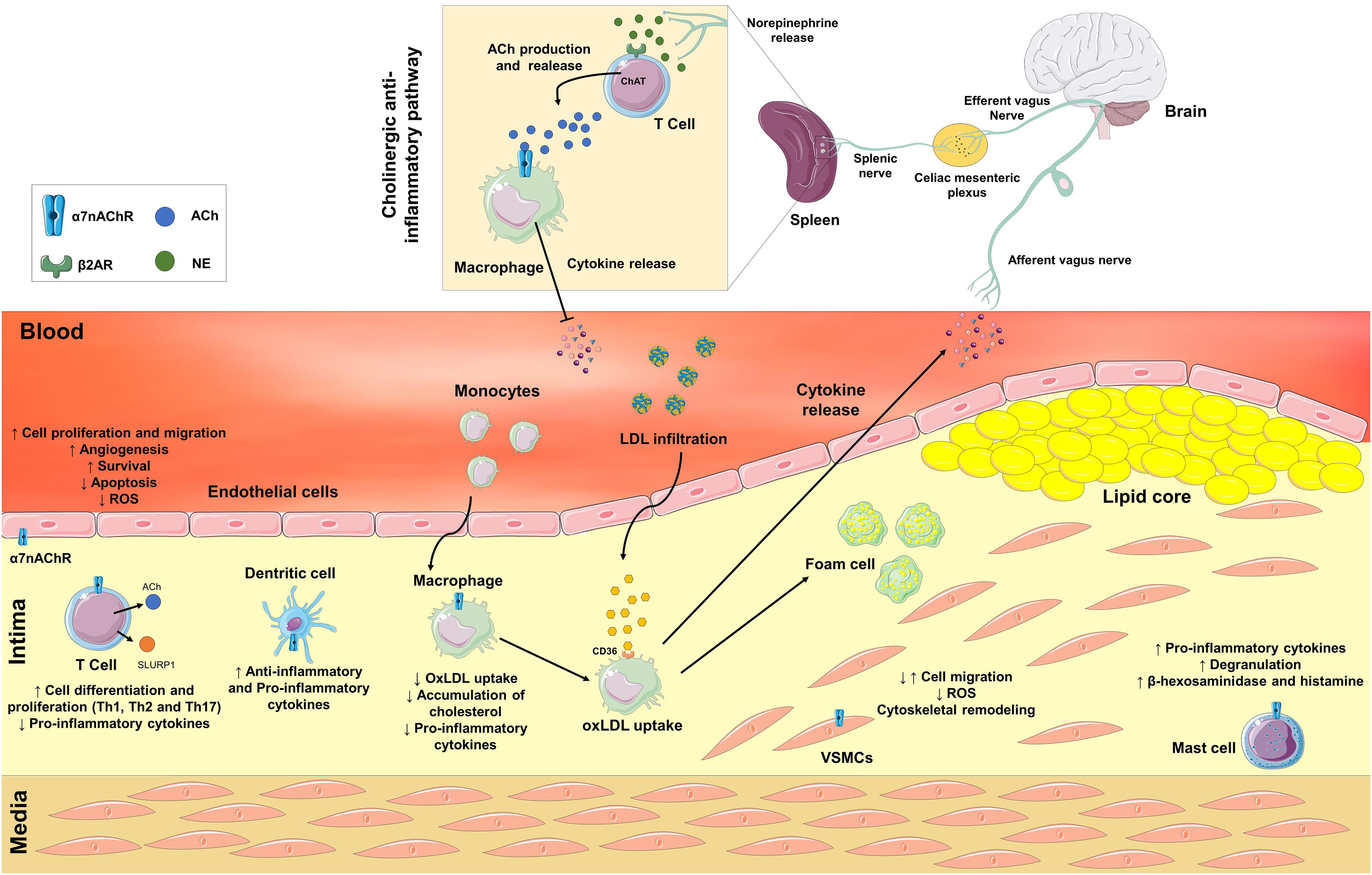
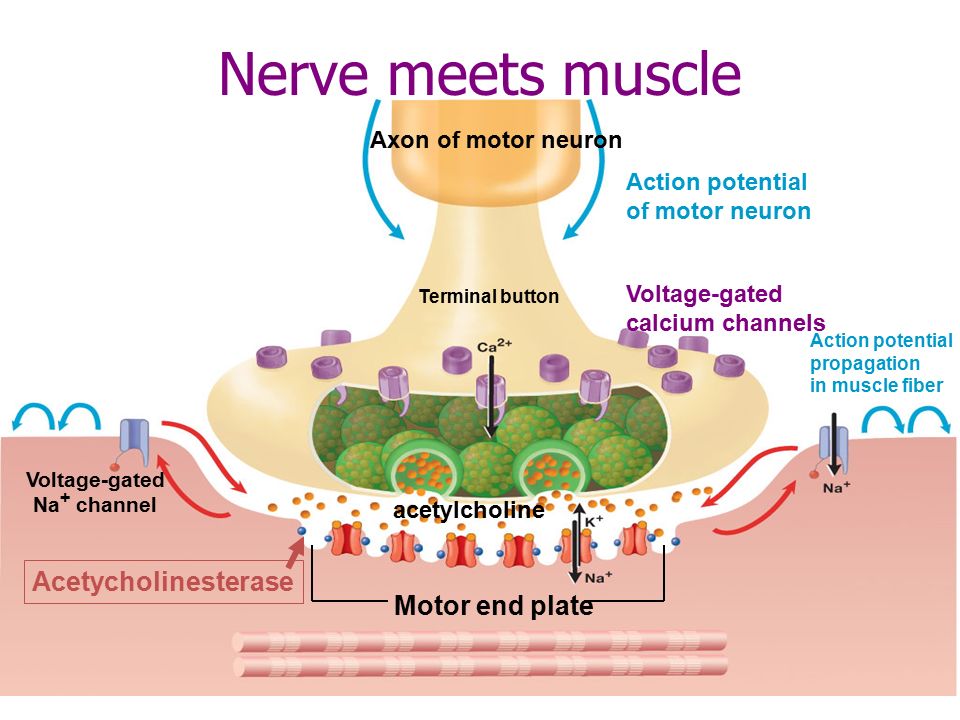
What Is The Role Of Acetylcholine In Calcium Release - In striated muscle, the increase in calcium levels is due to its release from the sr stores via ryanodine receptor (ryrs). Acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction relies on rapid, local and transient calcium increase at presynaptic active zones, triggered by the ion. The correlation of the shape of the action potential waveform with calcium current is effectively a balance between opening more calcium channels,. Upon entering a presynaptic terminal, an action potential opens ca 2+ channels, and transiently increases the local ca 2+ concentration at the. Ach release is triggered by calcium influx through specific presynaptic ca2+ channels. The modulation of this calcium influx appears as the main.
The modulation of this calcium influx appears as the main. The correlation of the shape of the action potential waveform with calcium current is effectively a balance between opening more calcium channels,. In striated muscle, the increase in calcium levels is due to its release from the sr stores via ryanodine receptor (ryrs). Upon entering a presynaptic terminal, an action potential opens ca 2+ channels, and transiently increases the local ca 2+ concentration at the. Ach release is triggered by calcium influx through specific presynaptic ca2+ channels. Acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction relies on rapid, local and transient calcium increase at presynaptic active zones, triggered by the ion.
Acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction relies on rapid, local and transient calcium increase at presynaptic active zones, triggered by the ion. The modulation of this calcium influx appears as the main. In striated muscle, the increase in calcium levels is due to its release from the sr stores via ryanodine receptor (ryrs). Upon entering a presynaptic terminal, an action potential opens ca 2+ channels, and transiently increases the local ca 2+ concentration at the. Ach release is triggered by calcium influx through specific presynaptic ca2+ channels. The correlation of the shape of the action potential waveform with calcium current is effectively a balance between opening more calcium channels,.
Acetylcholine Synthesis Pathway
In striated muscle, the increase in calcium levels is due to its release from the sr stores via ryanodine receptor (ryrs). Acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction relies on rapid, local and transient calcium increase at presynaptic active zones, triggered by the ion. The correlation of the shape of the action potential waveform with calcium current is effectively a balance.
Question Video Outlining the Role of Acetylcholine at a Neuromuscular
The correlation of the shape of the action potential waveform with calcium current is effectively a balance between opening more calcium channels,. Ach release is triggered by calcium influx through specific presynaptic ca2+ channels. Acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction relies on rapid, local and transient calcium increase at presynaptic active zones, triggered by the ion. Upon entering a presynaptic.
Pin on Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue
Upon entering a presynaptic terminal, an action potential opens ca 2+ channels, and transiently increases the local ca 2+ concentration at the. The modulation of this calcium influx appears as the main. The correlation of the shape of the action potential waveform with calcium current is effectively a balance between opening more calcium channels,. Ach release is triggered by calcium.
MUSCLE CONTRACTION (ACETYLCHOLINE) CELL COMMUNICATION Infogram
The correlation of the shape of the action potential waveform with calcium current is effectively a balance between opening more calcium channels,. Acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction relies on rapid, local and transient calcium increase at presynaptic active zones, triggered by the ion. Ach release is triggered by calcium influx through specific presynaptic ca2+ channels. The modulation of this.
9.3 Muscle Fiber Contraction and Relaxation Biomechanics of Human
The modulation of this calcium influx appears as the main. Upon entering a presynaptic terminal, an action potential opens ca 2+ channels, and transiently increases the local ca 2+ concentration at the. Acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction relies on rapid, local and transient calcium increase at presynaptic active zones, triggered by the ion. The correlation of the shape of.
What neurotransmitter stimulates skeletal muscle contraction? Socratic
Acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction relies on rapid, local and transient calcium increase at presynaptic active zones, triggered by the ion. The correlation of the shape of the action potential waveform with calcium current is effectively a balance between opening more calcium channels,. Upon entering a presynaptic terminal, an action potential opens ca 2+ channels, and transiently increases the.
Neurotransmitters Acetylcholine Introduction to Neuroscience
Upon entering a presynaptic terminal, an action potential opens ca 2+ channels, and transiently increases the local ca 2+ concentration at the. The modulation of this calcium influx appears as the main. In striated muscle, the increase in calcium levels is due to its release from the sr stores via ryanodine receptor (ryrs). Acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction relies.
Calcium Regulation Of Contraction Specialized Cell Muscle Cell MCAT
The modulation of this calcium influx appears as the main. Acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction relies on rapid, local and transient calcium increase at presynaptic active zones, triggered by the ion. In striated muscle, the increase in calcium levels is due to its release from the sr stores via ryanodine receptor (ryrs). Ach release is triggered by calcium influx.
Schematic representation of the acetylcholine synthesis, release, and
The correlation of the shape of the action potential waveform with calcium current is effectively a balance between opening more calcium channels,. The modulation of this calcium influx appears as the main. Acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction relies on rapid, local and transient calcium increase at presynaptic active zones, triggered by the ion. Upon entering a presynaptic terminal, an.
Acetylcholine biological vector illustration infographic diagram
The correlation of the shape of the action potential waveform with calcium current is effectively a balance between opening more calcium channels,. Upon entering a presynaptic terminal, an action potential opens ca 2+ channels, and transiently increases the local ca 2+ concentration at the. Acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction relies on rapid, local and transient calcium increase at presynaptic.
In Striated Muscle, The Increase In Calcium Levels Is Due To Its Release From The Sr Stores Via Ryanodine Receptor (Ryrs).
The modulation of this calcium influx appears as the main. Acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction relies on rapid, local and transient calcium increase at presynaptic active zones, triggered by the ion. Upon entering a presynaptic terminal, an action potential opens ca 2+ channels, and transiently increases the local ca 2+ concentration at the. Ach release is triggered by calcium influx through specific presynaptic ca2+ channels.