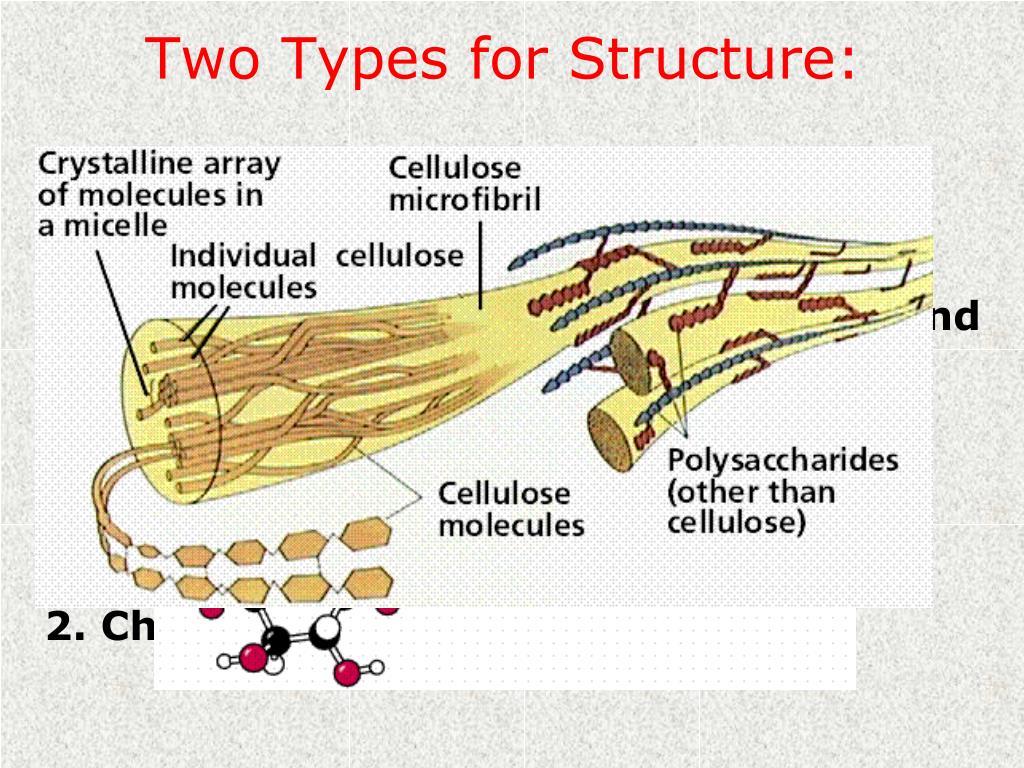
The Polysaccharide That Forms Plant Cell Walls Is - Often, other polymers such as. New technologies reveal the deposition and remodeling of plant cell wall polysaccharides and their impact on plant development. In land plants, the primary cell wall comprises polysaccharides like cellulose, hemicelluloses, and pectin. In addition to cellulose, plant cell walls contain several matrix polysaccharides that are grouped into two general categories: Cellulose, long crystals of several dozen glucan chains, forms the microfibrillar foundation of plant cell walls and is synthesized at the plasma. Plant cell walls are complex networks comprised of physically interacting polymers such as polysaccharides (pectin,. Cellulose, a major component of plant cell walls, is made by dynamic complexes that move within the plasma membrane while. The polysaccharides are the most abundant carbohydrates in nature and serve a variety of functions, such as energy storage or. Plant cells build nanofibrillar walls that are central to plant growth, morphogenesis and mechanics.
In land plants, the primary cell wall comprises polysaccharides like cellulose, hemicelluloses, and pectin. New technologies reveal the deposition and remodeling of plant cell wall polysaccharides and their impact on plant development. Cellulose, long crystals of several dozen glucan chains, forms the microfibrillar foundation of plant cell walls and is synthesized at the plasma. The polysaccharides are the most abundant carbohydrates in nature and serve a variety of functions, such as energy storage or. Often, other polymers such as. Plant cells build nanofibrillar walls that are central to plant growth, morphogenesis and mechanics. In addition to cellulose, plant cell walls contain several matrix polysaccharides that are grouped into two general categories: Plant cell walls are complex networks comprised of physically interacting polymers such as polysaccharides (pectin,. Cellulose, a major component of plant cell walls, is made by dynamic complexes that move within the plasma membrane while.
New technologies reveal the deposition and remodeling of plant cell wall polysaccharides and their impact on plant development. In addition to cellulose, plant cell walls contain several matrix polysaccharides that are grouped into two general categories: Often, other polymers such as. Plant cell walls are complex networks comprised of physically interacting polymers such as polysaccharides (pectin,. Cellulose, a major component of plant cell walls, is made by dynamic complexes that move within the plasma membrane while. Cellulose, long crystals of several dozen glucan chains, forms the microfibrillar foundation of plant cell walls and is synthesized at the plasma. In land plants, the primary cell wall comprises polysaccharides like cellulose, hemicelluloses, and pectin. The polysaccharides are the most abundant carbohydrates in nature and serve a variety of functions, such as energy storage or. Plant cells build nanofibrillar walls that are central to plant growth, morphogenesis and mechanics.
Biochemistry diagram present structure of polysaccharide such as starch
Cellulose, long crystals of several dozen glucan chains, forms the microfibrillar foundation of plant cell walls and is synthesized at the plasma. In addition to cellulose, plant cell walls contain several matrix polysaccharides that are grouped into two general categories: Plant cell walls are complex networks comprised of physically interacting polymers such as polysaccharides (pectin,. In land plants, the primary.
(PDF) Biochemistry and physiological roles of enzymes that ‘cut and
Cellulose, a major component of plant cell walls, is made by dynamic complexes that move within the plasma membrane while. Plant cells build nanofibrillar walls that are central to plant growth, morphogenesis and mechanics. New technologies reveal the deposition and remodeling of plant cell wall polysaccharides and their impact on plant development. In addition to cellulose, plant cell walls contain.
Exploring the polysaccharide composition of plant cell walls in
Plant cell walls are complex networks comprised of physically interacting polymers such as polysaccharides (pectin,. Often, other polymers such as. Cellulose, long crystals of several dozen glucan chains, forms the microfibrillar foundation of plant cell walls and is synthesized at the plasma. In addition to cellulose, plant cell walls contain several matrix polysaccharides that are grouped into two general categories:.
Plant cellulose biology vector illustration diagram Plant cell, Cell
Plant cells build nanofibrillar walls that are central to plant growth, morphogenesis and mechanics. In land plants, the primary cell wall comprises polysaccharides like cellulose, hemicelluloses, and pectin. Cellulose, long crystals of several dozen glucan chains, forms the microfibrillar foundation of plant cell walls and is synthesized at the plasma. New technologies reveal the deposition and remodeling of plant cell.
SOLVED Which polysaccharide forms the long, tough fibers found in
Cellulose, long crystals of several dozen glucan chains, forms the microfibrillar foundation of plant cell walls and is synthesized at the plasma. The polysaccharides are the most abundant carbohydrates in nature and serve a variety of functions, such as energy storage or. Often, other polymers such as. In land plants, the primary cell wall comprises polysaccharides like cellulose, hemicelluloses, and.
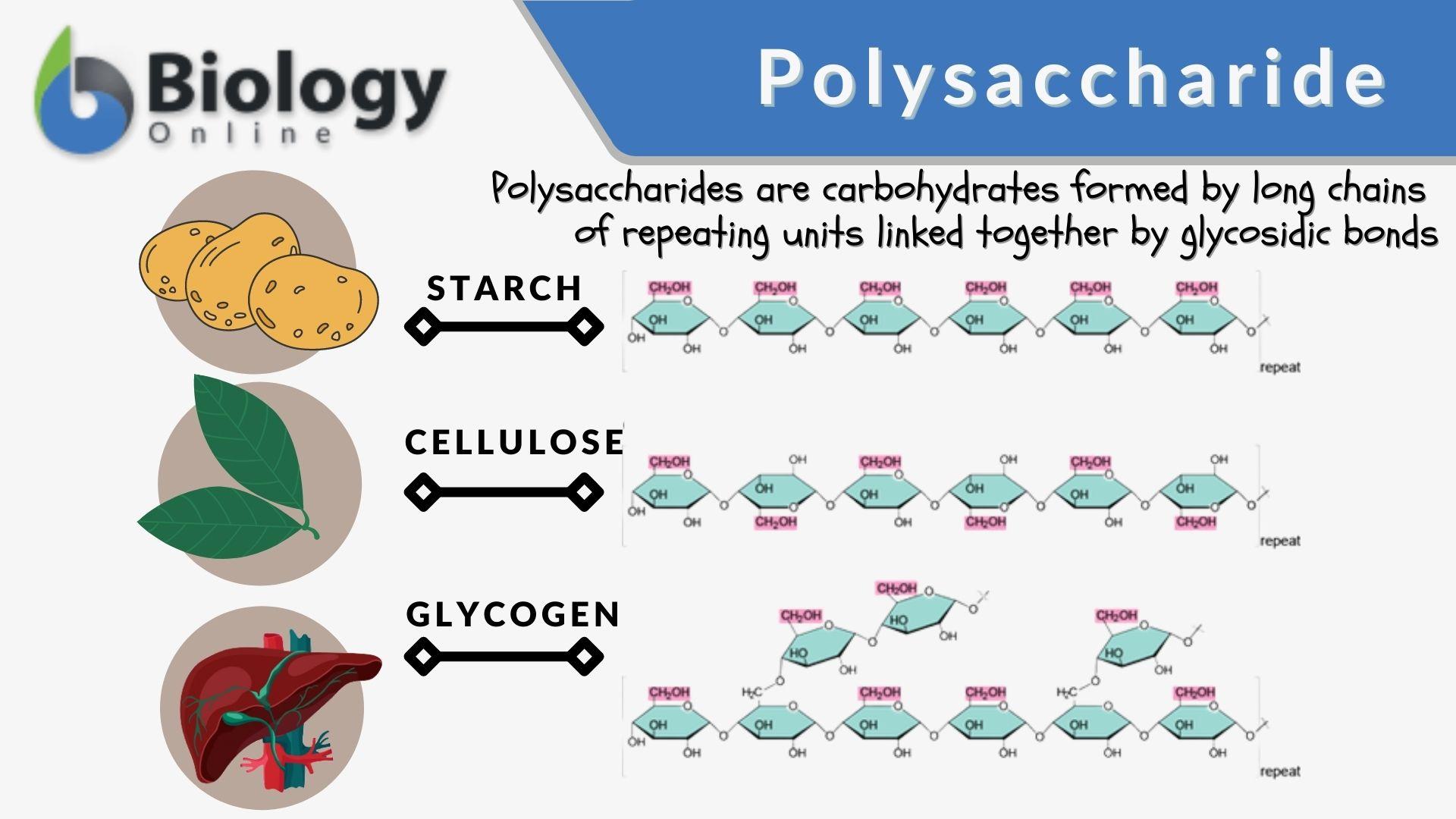
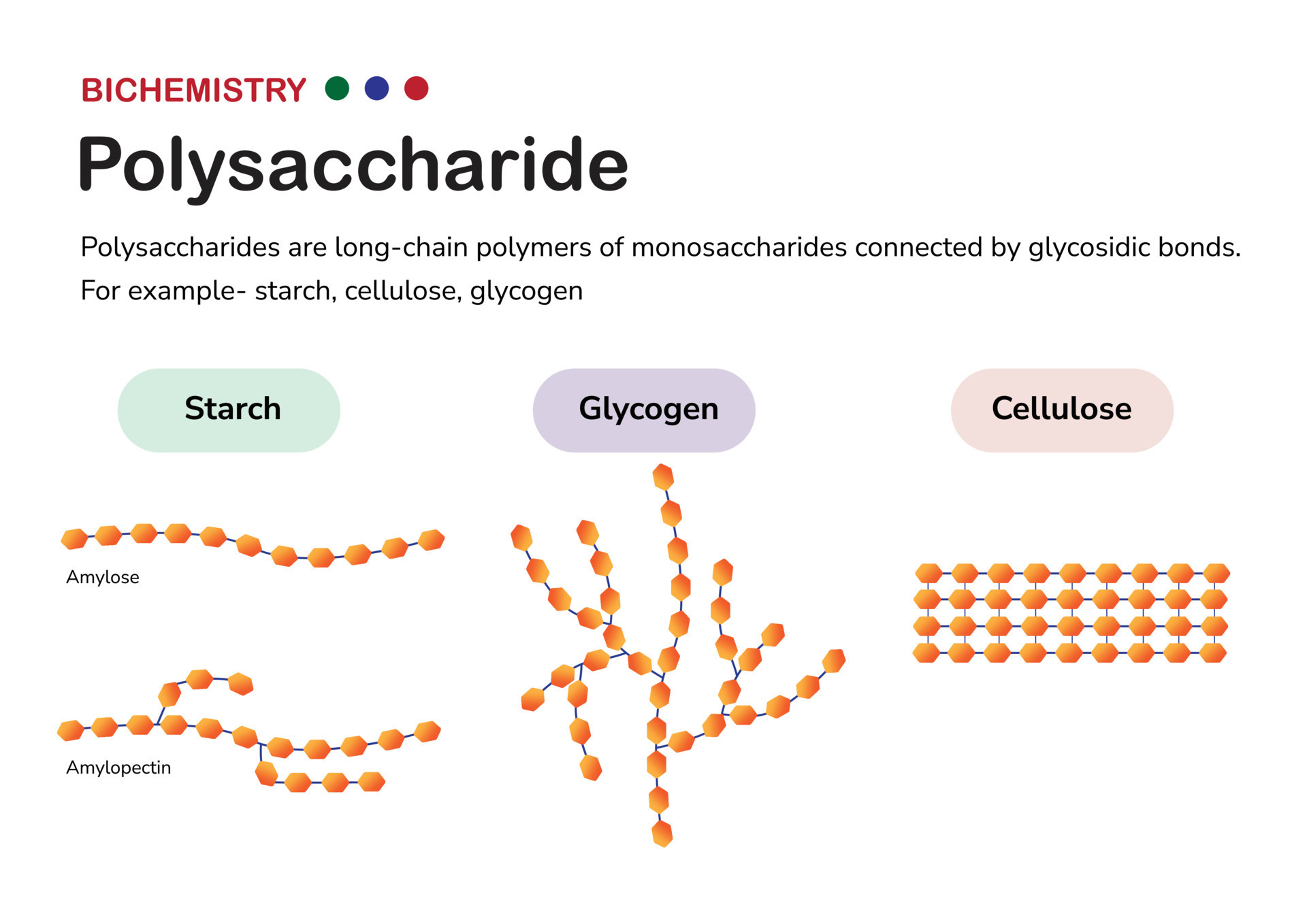
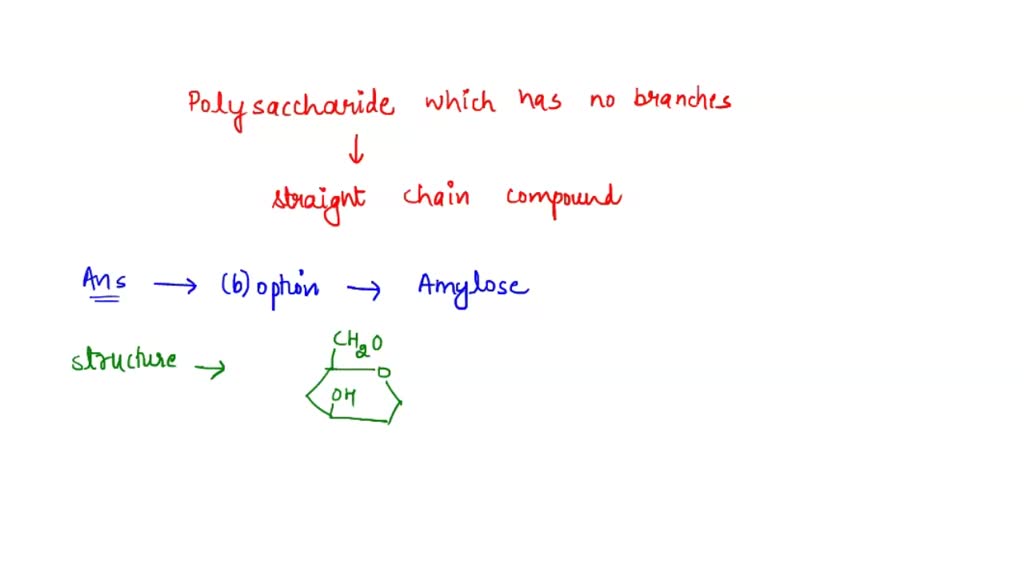
Polysaccharide
In land plants, the primary cell wall comprises polysaccharides like cellulose, hemicelluloses, and pectin. In addition to cellulose, plant cell walls contain several matrix polysaccharides that are grouped into two general categories: New technologies reveal the deposition and remodeling of plant cell wall polysaccharides and their impact on plant development. Plant cells build nanofibrillar walls that are central to plant.
Polysaccharide Definition and Functions
The polysaccharides are the most abundant carbohydrates in nature and serve a variety of functions, such as energy storage or. Cellulose, long crystals of several dozen glucan chains, forms the microfibrillar foundation of plant cell walls and is synthesized at the plasma. In addition to cellulose, plant cell walls contain several matrix polysaccharides that are grouped into two general categories:.
PPT Biomolecules PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1091680
In addition to cellulose, plant cell walls contain several matrix polysaccharides that are grouped into two general categories: The polysaccharides are the most abundant carbohydrates in nature and serve a variety of functions, such as energy storage or. Plant cells build nanofibrillar walls that are central to plant growth, morphogenesis and mechanics. In land plants, the primary cell wall comprises.
Polysaccharide Diagram
Cellulose, a major component of plant cell walls, is made by dynamic complexes that move within the plasma membrane while. In addition to cellulose, plant cell walls contain several matrix polysaccharides that are grouped into two general categories: The polysaccharides are the most abundant carbohydrates in nature and serve a variety of functions, such as energy storage or. In land.
Energy Storage Form Of Carbohydrates In Animals Printable Form
In land plants, the primary cell wall comprises polysaccharides like cellulose, hemicelluloses, and pectin. New technologies reveal the deposition and remodeling of plant cell wall polysaccharides and their impact on plant development. Cellulose, a major component of plant cell walls, is made by dynamic complexes that move within the plasma membrane while. Often, other polymers such as. Cellulose, long crystals.
Plant Cell Walls Are Complex Networks Comprised Of Physically Interacting Polymers Such As Polysaccharides (Pectin,.
Often, other polymers such as. New technologies reveal the deposition and remodeling of plant cell wall polysaccharides and their impact on plant development. Cellulose, a major component of plant cell walls, is made by dynamic complexes that move within the plasma membrane while. The polysaccharides are the most abundant carbohydrates in nature and serve a variety of functions, such as energy storage or.
In Addition To Cellulose, Plant Cell Walls Contain Several Matrix Polysaccharides That Are Grouped Into Two General Categories:
Plant cells build nanofibrillar walls that are central to plant growth, morphogenesis and mechanics. Cellulose, long crystals of several dozen glucan chains, forms the microfibrillar foundation of plant cell walls and is synthesized at the plasma. In land plants, the primary cell wall comprises polysaccharides like cellulose, hemicelluloses, and pectin.



/GettyImages-1193686961-055bb7e250ca44eb817d245b301a0bf4.jpg)