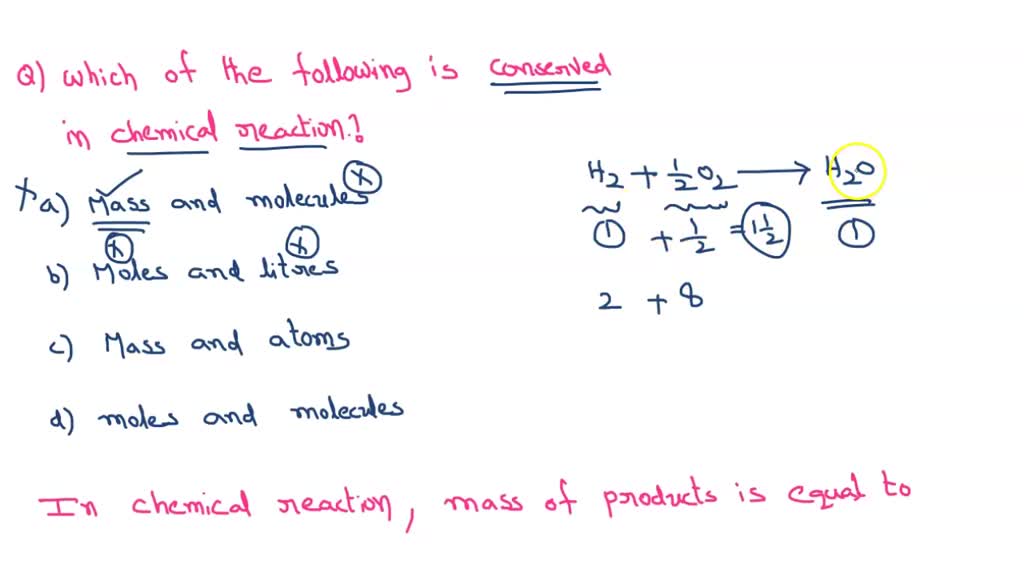
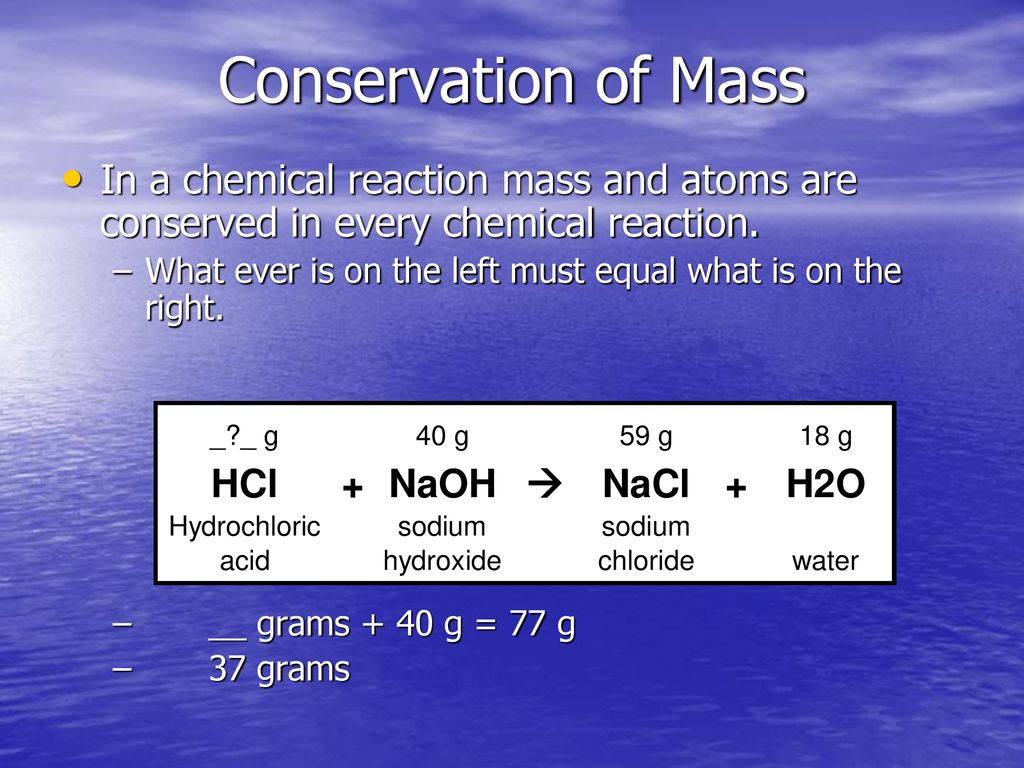
In Every Chemical Reaction What Is Conserved - Let’s analyze a few rows of the above table, beginning with row a. The reactant that determines the amount of product that can be formed in a reaction. In every chemical reaction, the same mass of matter must end up in the products as started in the reactants. The law of conservation of matter says that in chemical reactions, the total mass of the products must equal the total mass of the reactants. This is conserved in every ordinary chemical reaction. Picture the reactants n 2 and h 2 as being the initial.
Picture the reactants n 2 and h 2 as being the initial. Let’s analyze a few rows of the above table, beginning with row a. The law of conservation of matter says that in chemical reactions, the total mass of the products must equal the total mass of the reactants. This is conserved in every ordinary chemical reaction. In every chemical reaction, the same mass of matter must end up in the products as started in the reactants. The reactant that determines the amount of product that can be formed in a reaction.
The reactant that determines the amount of product that can be formed in a reaction. Picture the reactants n 2 and h 2 as being the initial. In every chemical reaction, the same mass of matter must end up in the products as started in the reactants. The law of conservation of matter says that in chemical reactions, the total mass of the products must equal the total mass of the reactants. Let’s analyze a few rows of the above table, beginning with row a. This is conserved in every ordinary chemical reaction.
Stoichiometry moltomol ratios ppt download
The law of conservation of matter says that in chemical reactions, the total mass of the products must equal the total mass of the reactants. This is conserved in every ordinary chemical reaction. Picture the reactants n 2 and h 2 as being the initial. Let’s analyze a few rows of the above table, beginning with row a. The reactant.
Stoichiometry Chapter ppt download
This is conserved in every ordinary chemical reaction. Picture the reactants n 2 and h 2 as being the initial. In every chemical reaction, the same mass of matter must end up in the products as started in the reactants. Let’s analyze a few rows of the above table, beginning with row a. The reactant that determines the amount of.
Drill What is a chemical reaction What is
Picture the reactants n 2 and h 2 as being the initial. Let’s analyze a few rows of the above table, beginning with row a. The law of conservation of matter says that in chemical reactions, the total mass of the products must equal the total mass of the reactants. In every chemical reaction, the same mass of matter must.
SOLVED Which of the following are CONSERVED in every chemical reaction
Picture the reactants n 2 and h 2 as being the initial. This is conserved in every ordinary chemical reaction. The reactant that determines the amount of product that can be formed in a reaction. In every chemical reaction, the same mass of matter must end up in the products as started in the reactants. The law of conservation of.
What Is Conserved in Chemical Reactions? Sciencing
In every chemical reaction, the same mass of matter must end up in the products as started in the reactants. Let’s analyze a few rows of the above table, beginning with row a. The law of conservation of matter says that in chemical reactions, the total mass of the products must equal the total mass of the reactants. This is.
Stoichiometry ICS III Week ppt download
The law of conservation of matter says that in chemical reactions, the total mass of the products must equal the total mass of the reactants. Let’s analyze a few rows of the above table, beginning with row a. In every chemical reaction, the same mass of matter must end up in the products as started in the reactants. Picture the.
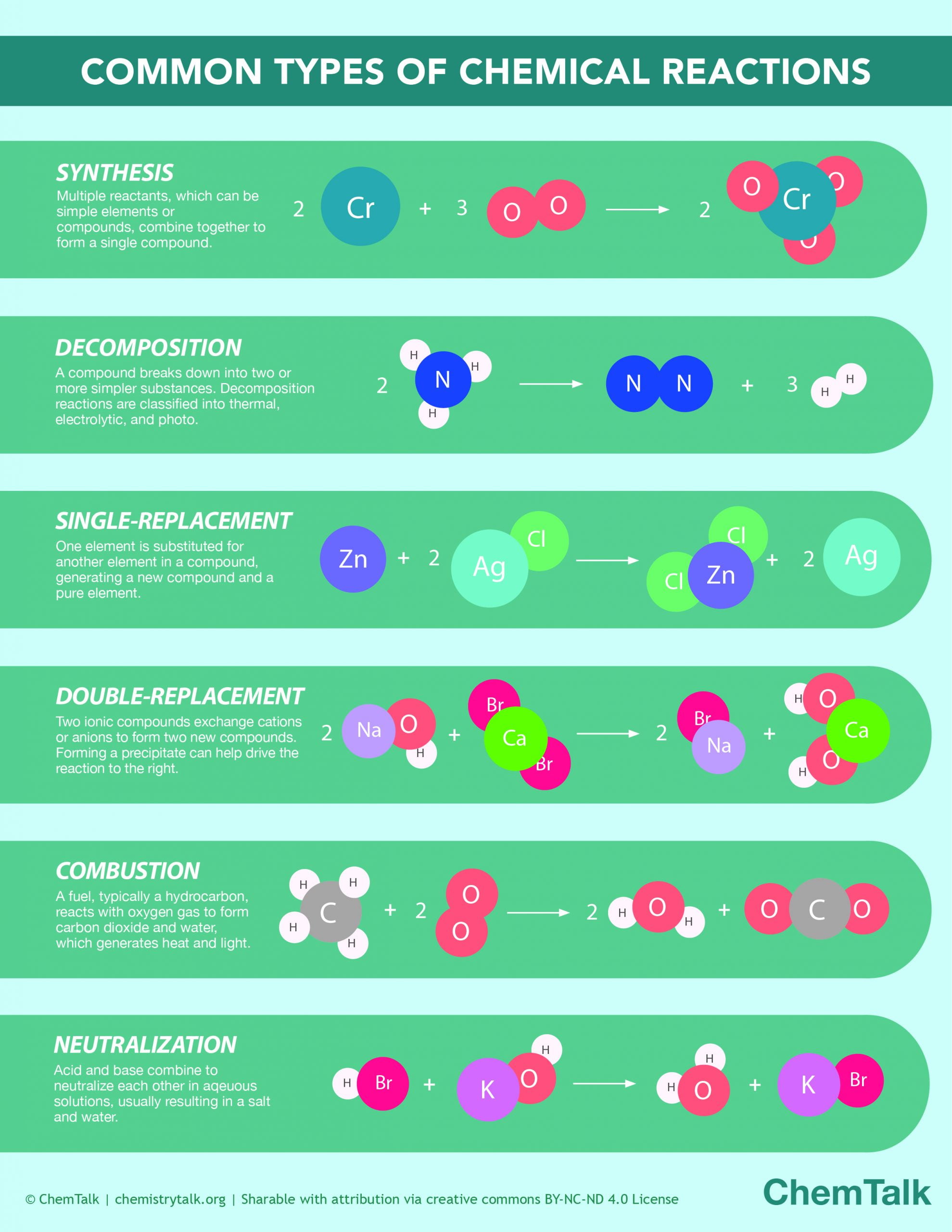
Chemical Reactions Infographic ChemTalk
Picture the reactants n 2 and h 2 as being the initial. Let’s analyze a few rows of the above table, beginning with row a. In every chemical reaction, the same mass of matter must end up in the products as started in the reactants. The reactant that determines the amount of product that can be formed in a reaction..
Stoichiometry Notes. In every chemical reaction, the mass and number of
In every chemical reaction, the same mass of matter must end up in the products as started in the reactants. Picture the reactants n 2 and h 2 as being the initial. The reactant that determines the amount of product that can be formed in a reaction. The law of conservation of matter says that in chemical reactions, the total.
Review When converting FROM moles you MULTIPLY. ppt download
Picture the reactants n 2 and h 2 as being the initial. The reactant that determines the amount of product that can be formed in a reaction. The law of conservation of matter says that in chemical reactions, the total mass of the products must equal the total mass of the reactants. This is conserved in every ordinary chemical reaction..
Chemical Reaction Definition, Types and Examples Class 10 Science
This is conserved in every ordinary chemical reaction. The law of conservation of matter says that in chemical reactions, the total mass of the products must equal the total mass of the reactants. The reactant that determines the amount of product that can be formed in a reaction. Let’s analyze a few rows of the above table, beginning with row.
The Reactant That Determines The Amount Of Product That Can Be Formed In A Reaction.
Let’s analyze a few rows of the above table, beginning with row a. The law of conservation of matter says that in chemical reactions, the total mass of the products must equal the total mass of the reactants. This is conserved in every ordinary chemical reaction. In every chemical reaction, the same mass of matter must end up in the products as started in the reactants.