Energy Is Stored In Muscle Cells In The Form Of - Muscle energy systems are essential mechanisms by which your muscles produce the energy required for physical activity. Normal metabolism can not produce energy as quickly as a muscle. Muscles store energy in various forms, primarily to be used during physical activity. Muscle fibers also contain glycogen granules as a stored energy source, and myofibrils, which are threadlike structures running the length. Muscle cells use this phosphorylated form of creatine to store energy. For the next ~30 min (but can be up to several hours for well trained endurance athletes), the muscle relies mainly on energy stored as. In addition to human muscle and liver cells, glycogen is stored in small amounts in brain cells, heart cells, smooth muscle cells, kidney cells, red and white. The main forms of energy storage are creatine phosphate, atp.
Muscles store energy in various forms, primarily to be used during physical activity. Muscle cells use this phosphorylated form of creatine to store energy. In addition to human muscle and liver cells, glycogen is stored in small amounts in brain cells, heart cells, smooth muscle cells, kidney cells, red and white. For the next ~30 min (but can be up to several hours for well trained endurance athletes), the muscle relies mainly on energy stored as. The main forms of energy storage are creatine phosphate, atp. Muscle energy systems are essential mechanisms by which your muscles produce the energy required for physical activity. Muscle fibers also contain glycogen granules as a stored energy source, and myofibrils, which are threadlike structures running the length. Normal metabolism can not produce energy as quickly as a muscle.
Muscles store energy in various forms, primarily to be used during physical activity. Normal metabolism can not produce energy as quickly as a muscle. Muscle fibers also contain glycogen granules as a stored energy source, and myofibrils, which are threadlike structures running the length. Muscle cells use this phosphorylated form of creatine to store energy. The main forms of energy storage are creatine phosphate, atp. Muscle energy systems are essential mechanisms by which your muscles produce the energy required for physical activity. In addition to human muscle and liver cells, glycogen is stored in small amounts in brain cells, heart cells, smooth muscle cells, kidney cells, red and white. For the next ~30 min (but can be up to several hours for well trained endurance athletes), the muscle relies mainly on energy stored as.
[LS17] Cellular Respiration and Energy Biology Dictionary
The main forms of energy storage are creatine phosphate, atp. Muscle energy systems are essential mechanisms by which your muscles produce the energy required for physical activity. Normal metabolism can not produce energy as quickly as a muscle. In addition to human muscle and liver cells, glycogen is stored in small amounts in brain cells, heart cells, smooth muscle cells,.
Arkα. on Twitter "Buff reaper Physis. He trains himself regularly to
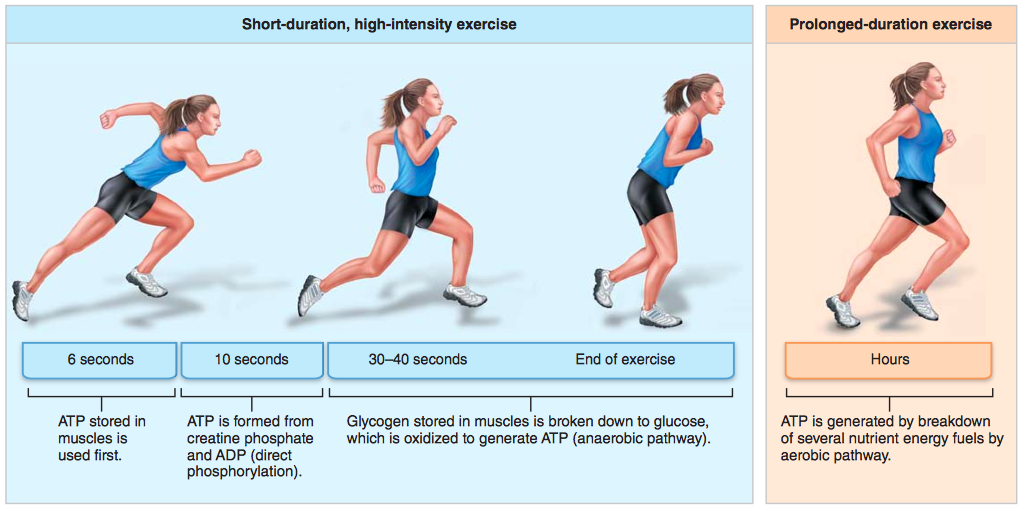
For the next ~30 min (but can be up to several hours for well trained endurance athletes), the muscle relies mainly on energy stored as. Normal metabolism can not produce energy as quickly as a muscle. Muscles store energy in various forms, primarily to be used during physical activity. Muscle cells use this phosphorylated form of creatine to store energy..
Muscle Glycogen and Exercise all you need to know INSCYD
Muscle fibers also contain glycogen granules as a stored energy source, and myofibrils, which are threadlike structures running the length. Normal metabolism can not produce energy as quickly as a muscle. The main forms of energy storage are creatine phosphate, atp. Muscles store energy in various forms, primarily to be used during physical activity. For the next ~30 min (but.
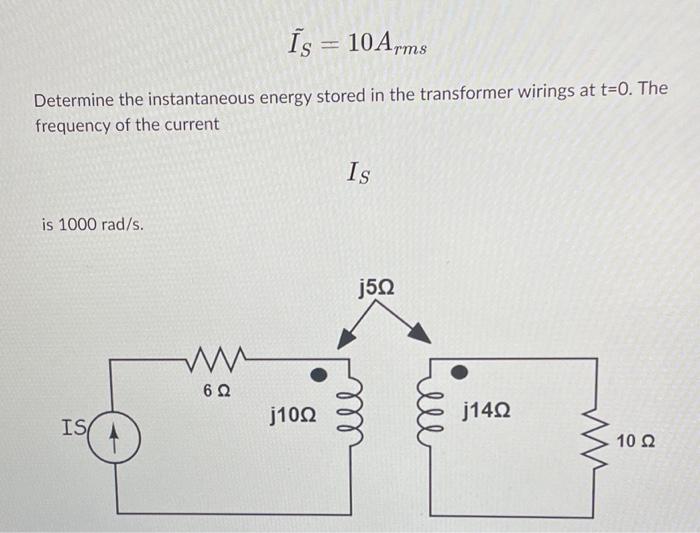
Solved IS=10Arms Determine the instantaneous energy stored
Muscle energy systems are essential mechanisms by which your muscles produce the energy required for physical activity. Muscle cells use this phosphorylated form of creatine to store energy. Muscle fibers also contain glycogen granules as a stored energy source, and myofibrils, which are threadlike structures running the length. Normal metabolism can not produce energy as quickly as a muscle. In.
Energy for Contractions ms. gallagher's classroom
Muscle energy systems are essential mechanisms by which your muscles produce the energy required for physical activity. Muscle fibers also contain glycogen granules as a stored energy source, and myofibrils, which are threadlike structures running the length. In addition to human muscle and liver cells, glycogen is stored in small amounts in brain cells, heart cells, smooth muscle cells, kidney.
PPT Energy in the Cell PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Muscle fibers also contain glycogen granules as a stored energy source, and myofibrils, which are threadlike structures running the length. The main forms of energy storage are creatine phosphate, atp. Normal metabolism can not produce energy as quickly as a muscle. For the next ~30 min (but can be up to several hours for well trained endurance athletes), the muscle.
PPT Carbohydrate Metabolism 2 Glycogen degradation, glycogen
Normal metabolism can not produce energy as quickly as a muscle. In addition to human muscle and liver cells, glycogen is stored in small amounts in brain cells, heart cells, smooth muscle cells, kidney cells, red and white. Muscle fibers also contain glycogen granules as a stored energy source, and myofibrils, which are threadlike structures running the length. Muscle energy.
Anaerobic Respiration In Plants Equation Physical
Normal metabolism can not produce energy as quickly as a muscle. In addition to human muscle and liver cells, glycogen is stored in small amounts in brain cells, heart cells, smooth muscle cells, kidney cells, red and white. Muscle cells use this phosphorylated form of creatine to store energy. For the next ~30 min (but can be up to several.
13 Glucose Pyruvate Breakdown Images, Stock Photos & Vectors Shutterstock
For the next ~30 min (but can be up to several hours for well trained endurance athletes), the muscle relies mainly on energy stored as. Muscles store energy in various forms, primarily to be used during physical activity. Muscle fibers also contain glycogen granules as a stored energy source, and myofibrils, which are threadlike structures running the length. Muscle energy.
Glycogen Physiopedia
Muscle cells use this phosphorylated form of creatine to store energy. The main forms of energy storage are creatine phosphate, atp. For the next ~30 min (but can be up to several hours for well trained endurance athletes), the muscle relies mainly on energy stored as. Muscle fibers also contain glycogen granules as a stored energy source, and myofibrils, which.
Muscle Energy Systems Are Essential Mechanisms By Which Your Muscles Produce The Energy Required For Physical Activity.
In addition to human muscle and liver cells, glycogen is stored in small amounts in brain cells, heart cells, smooth muscle cells, kidney cells, red and white. Muscle cells use this phosphorylated form of creatine to store energy. Muscles store energy in various forms, primarily to be used during physical activity. The main forms of energy storage are creatine phosphate, atp.
Muscle Fibers Also Contain Glycogen Granules As A Stored Energy Source, And Myofibrils, Which Are Threadlike Structures Running The Length.
Normal metabolism can not produce energy as quickly as a muscle. For the next ~30 min (but can be up to several hours for well trained endurance athletes), the muscle relies mainly on energy stored as.
![[LS17] Cellular Respiration and Energy Biology Dictionary](https://biologydictionary.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/Glucose-molecule.jpg)