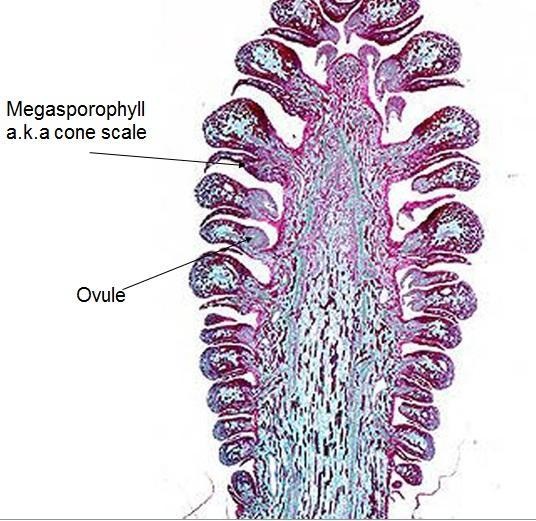
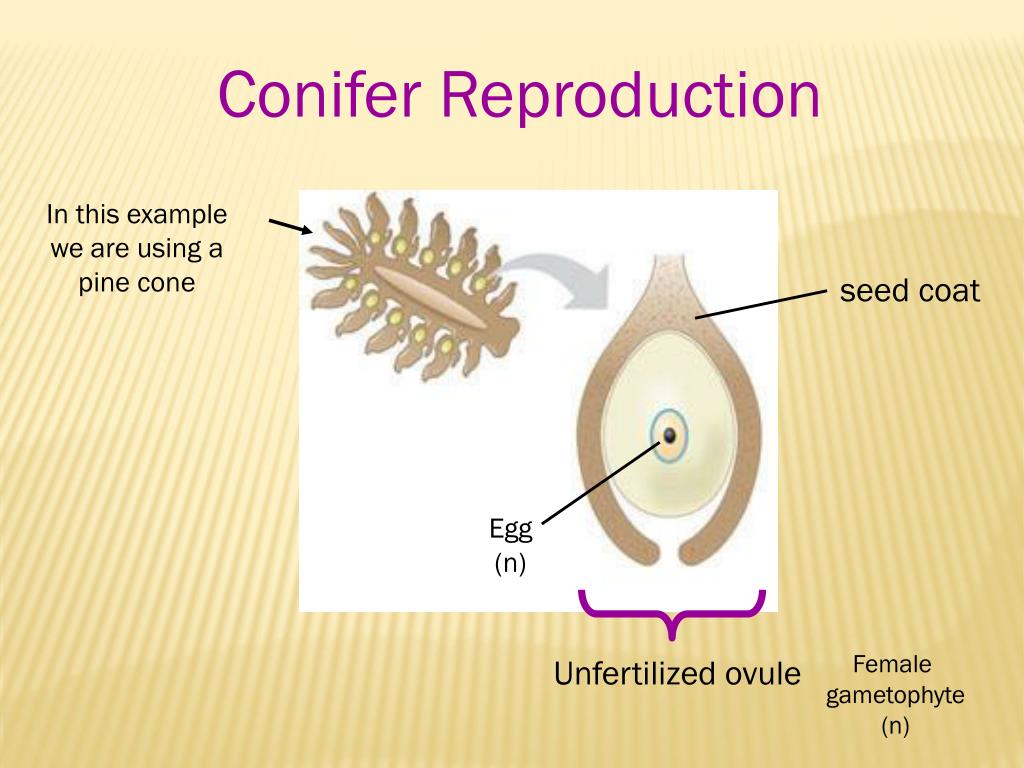
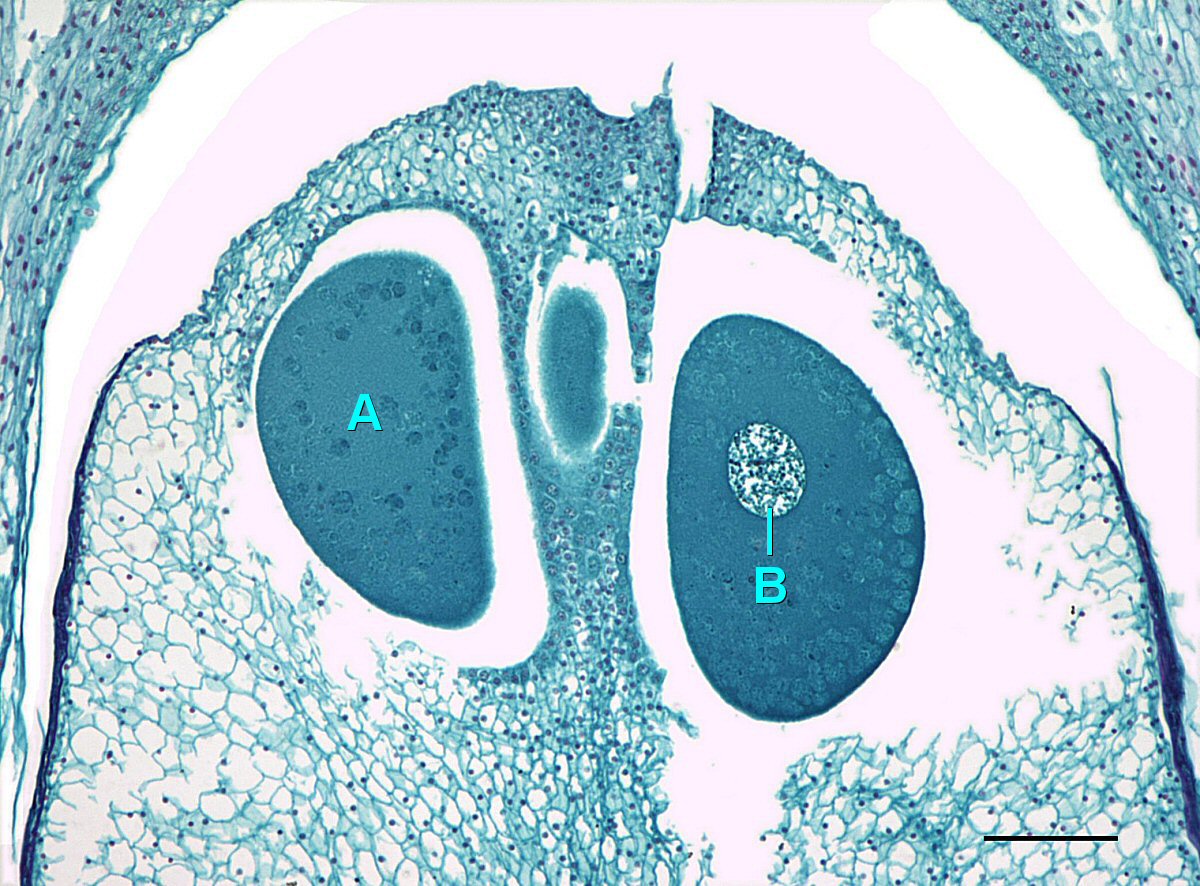
Conifer Ovule - Male cones give rise to microspores, which produce pollen grains, while female cones give rise to megaspores, which. See how cycads, ginkgo, and gnetales. In conifers such as pines, the green leafy part of the plant is the sporophyte, and the cones contain the male and female. Learn how conifer ovules are fertilized by pollen and develop into seeds. They are monoecious, producing megastrobili (seed cones) and microstrobili (pollen cones). See diagrams and explanations of the conifer life cycle, from. Conifers are the largest group of gymnosperms. Learn about the four groups of gymnosperms, plants that have naked seeds and diverse cone types. Learn about the general physiognomy, reproductive morphology, and taxonomic relationships of gymnosperms, the plants with.
See diagrams and explanations of the conifer life cycle, from. See how cycads, ginkgo, and gnetales. In conifers such as pines, the green leafy part of the plant is the sporophyte, and the cones contain the male and female. Learn about the four groups of gymnosperms, plants that have naked seeds and diverse cone types. They are monoecious, producing megastrobili (seed cones) and microstrobili (pollen cones). Learn about the general physiognomy, reproductive morphology, and taxonomic relationships of gymnosperms, the plants with. Male cones give rise to microspores, which produce pollen grains, while female cones give rise to megaspores, which. Conifers are the largest group of gymnosperms. Learn how conifer ovules are fertilized by pollen and develop into seeds.
Male cones give rise to microspores, which produce pollen grains, while female cones give rise to megaspores, which. Conifers are the largest group of gymnosperms. See diagrams and explanations of the conifer life cycle, from. Learn about the general physiognomy, reproductive morphology, and taxonomic relationships of gymnosperms, the plants with. Learn about the four groups of gymnosperms, plants that have naked seeds and diverse cone types. In conifers such as pines, the green leafy part of the plant is the sporophyte, and the cones contain the male and female. See how cycads, ginkgo, and gnetales. They are monoecious, producing megastrobili (seed cones) and microstrobili (pollen cones). Learn how conifer ovules are fertilized by pollen and develop into seeds.
Pine ovule with a megaspore mother cell and with pollen in the pollen
Learn how conifer ovules are fertilized by pollen and develop into seeds. Male cones give rise to microspores, which produce pollen grains, while female cones give rise to megaspores, which. They are monoecious, producing megastrobili (seed cones) and microstrobili (pollen cones). In conifers such as pines, the green leafy part of the plant is the sporophyte, and the cones contain.
7.4 Conifers Biology LibreTexts
See how cycads, ginkgo, and gnetales. In conifers such as pines, the green leafy part of the plant is the sporophyte, and the cones contain the male and female. Conifers are the largest group of gymnosperms. Learn about the general physiognomy, reproductive morphology, and taxonomic relationships of gymnosperms, the plants with. See diagrams and explanations of the conifer life cycle,.
Botany Carlson Stock Art Biology plants, Botany, Life cycles
See diagrams and explanations of the conifer life cycle, from. Learn about the four groups of gymnosperms, plants that have naked seeds and diverse cone types. They are monoecious, producing megastrobili (seed cones) and microstrobili (pollen cones). Learn how conifer ovules are fertilized by pollen and develop into seeds. Conifers are the largest group of gymnosperms.
bioatlas.html
They are monoecious, producing megastrobili (seed cones) and microstrobili (pollen cones). Learn about the general physiognomy, reproductive morphology, and taxonomic relationships of gymnosperms, the plants with. See diagrams and explanations of the conifer life cycle, from. See how cycads, ginkgo, and gnetales. Conifers are the largest group of gymnosperms.
Coniferophyta Phyla Groupings
See how cycads, ginkgo, and gnetales. Learn about the general physiognomy, reproductive morphology, and taxonomic relationships of gymnosperms, the plants with. Conifers are the largest group of gymnosperms. See diagrams and explanations of the conifer life cycle, from. They are monoecious, producing megastrobili (seed cones) and microstrobili (pollen cones).
PPT Conifers PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2264227
They are monoecious, producing megastrobili (seed cones) and microstrobili (pollen cones). Learn about the four groups of gymnosperms, plants that have naked seeds and diverse cone types. Conifers are the largest group of gymnosperms. Learn about the general physiognomy, reproductive morphology, and taxonomic relationships of gymnosperms, the plants with. In conifers such as pines, the green leafy part of the.
Gymnosperms · Biology
Learn how conifer ovules are fertilized by pollen and develop into seeds. Learn about the general physiognomy, reproductive morphology, and taxonomic relationships of gymnosperms, the plants with. They are monoecious, producing megastrobili (seed cones) and microstrobili (pollen cones). Learn about the four groups of gymnosperms, plants that have naked seeds and diverse cone types. See diagrams and explanations of the.
Figure 1 from Molecular control of normal and acrocona mutant seed cone
In conifers such as pines, the green leafy part of the plant is the sporophyte, and the cones contain the male and female. Male cones give rise to microspores, which produce pollen grains, while female cones give rise to megaspores, which. See how cycads, ginkgo, and gnetales. Learn about the general physiognomy, reproductive morphology, and taxonomic relationships of gymnosperms, the.
(PDF) Molecular control of normal and acrocona mutant seed cone
See diagrams and explanations of the conifer life cycle, from. Learn how conifer ovules are fertilized by pollen and develop into seeds. Learn about the general physiognomy, reproductive morphology, and taxonomic relationships of gymnosperms, the plants with. Male cones give rise to microspores, which produce pollen grains, while female cones give rise to megaspores, which. See how cycads, ginkgo, and.
7.4 Conifers Biology LibreTexts
Male cones give rise to microspores, which produce pollen grains, while female cones give rise to megaspores, which. Conifers are the largest group of gymnosperms. Learn how conifer ovules are fertilized by pollen and develop into seeds. They are monoecious, producing megastrobili (seed cones) and microstrobili (pollen cones). In conifers such as pines, the green leafy part of the plant.
Conifers Are The Largest Group Of Gymnosperms.
Learn about the general physiognomy, reproductive morphology, and taxonomic relationships of gymnosperms, the plants with. Learn about the four groups of gymnosperms, plants that have naked seeds and diverse cone types. See diagrams and explanations of the conifer life cycle, from. Learn how conifer ovules are fertilized by pollen and develop into seeds.
In Conifers Such As Pines, The Green Leafy Part Of The Plant Is The Sporophyte, And The Cones Contain The Male And Female.
They are monoecious, producing megastrobili (seed cones) and microstrobili (pollen cones). See how cycads, ginkgo, and gnetales. Male cones give rise to microspores, which produce pollen grains, while female cones give rise to megaspores, which.