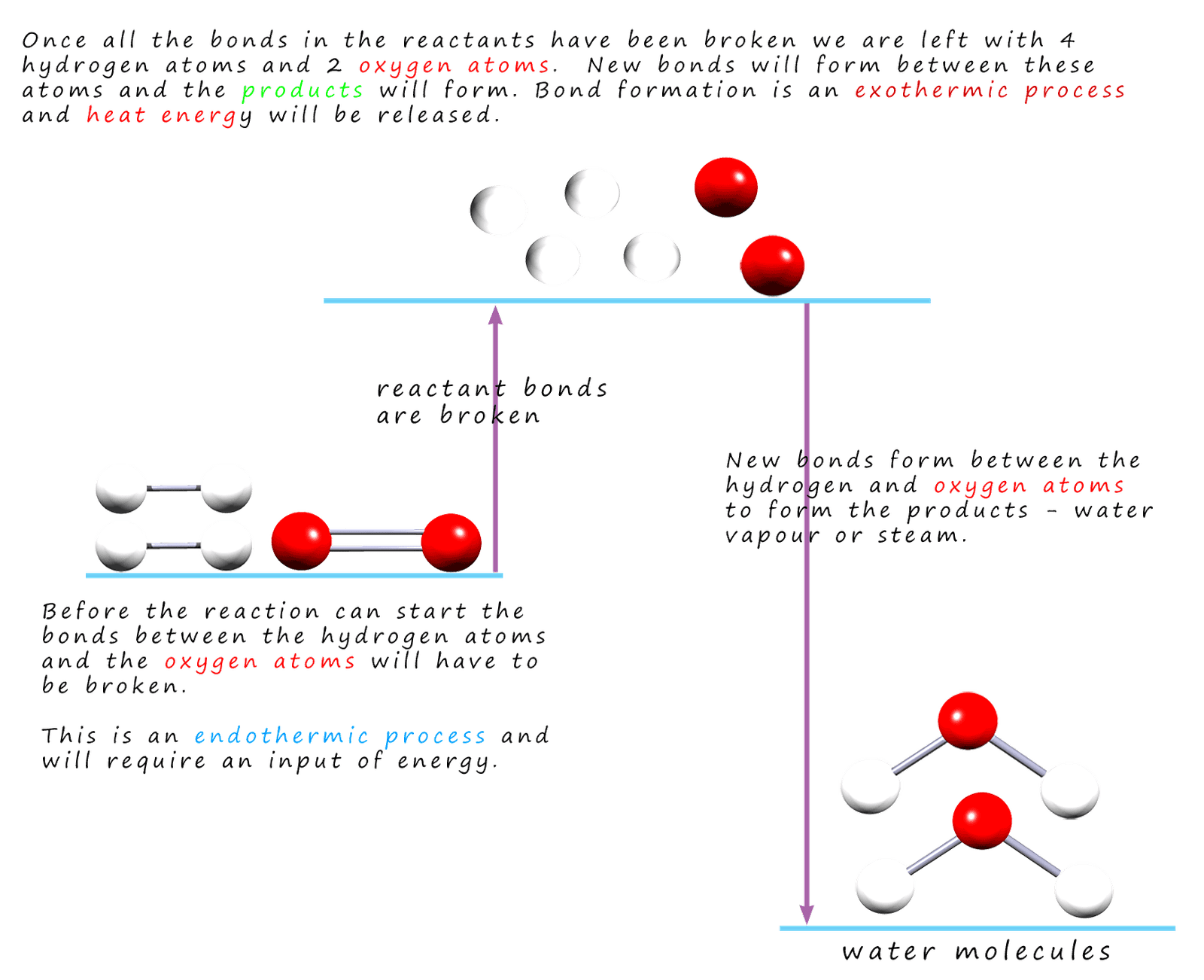
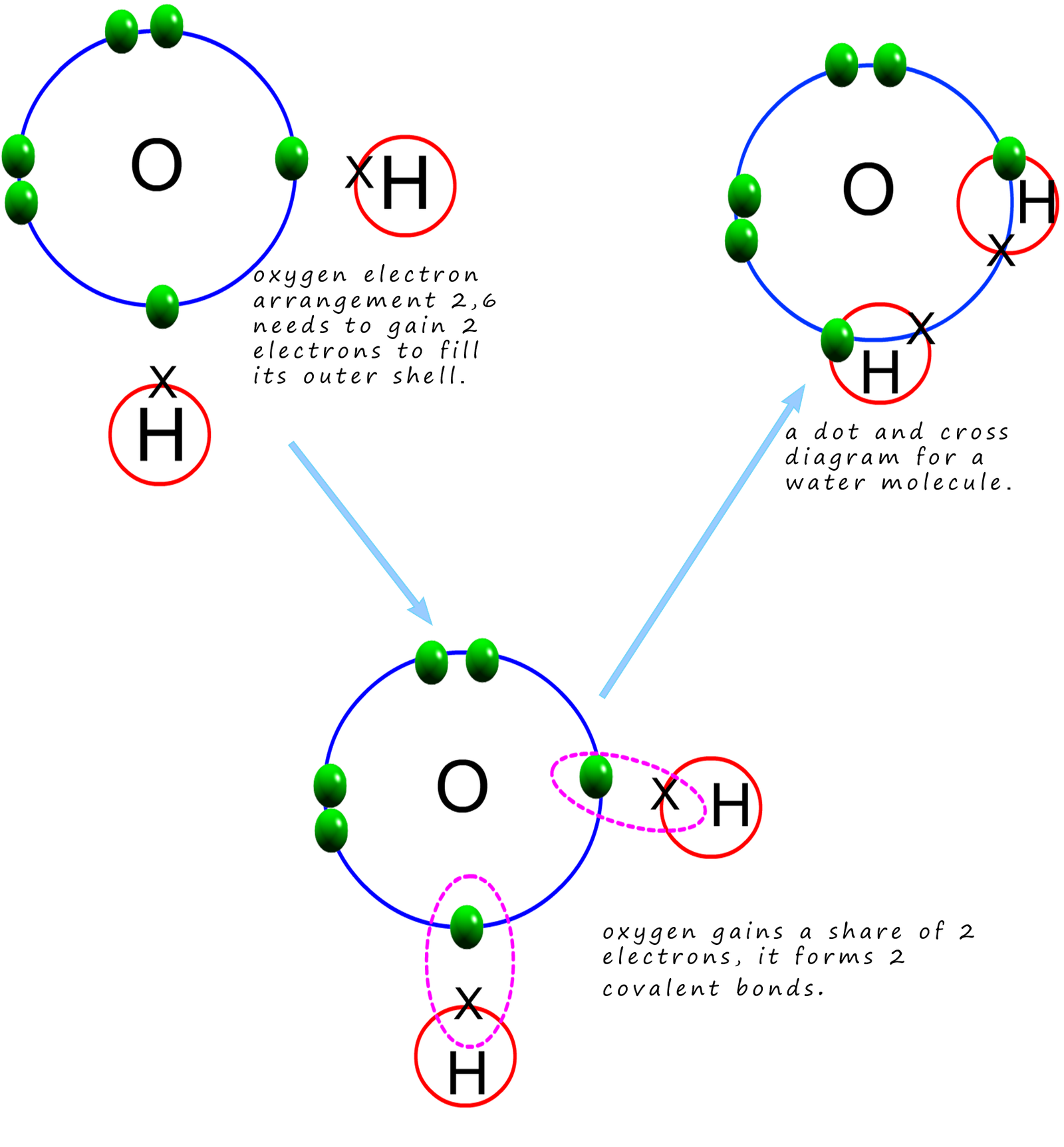
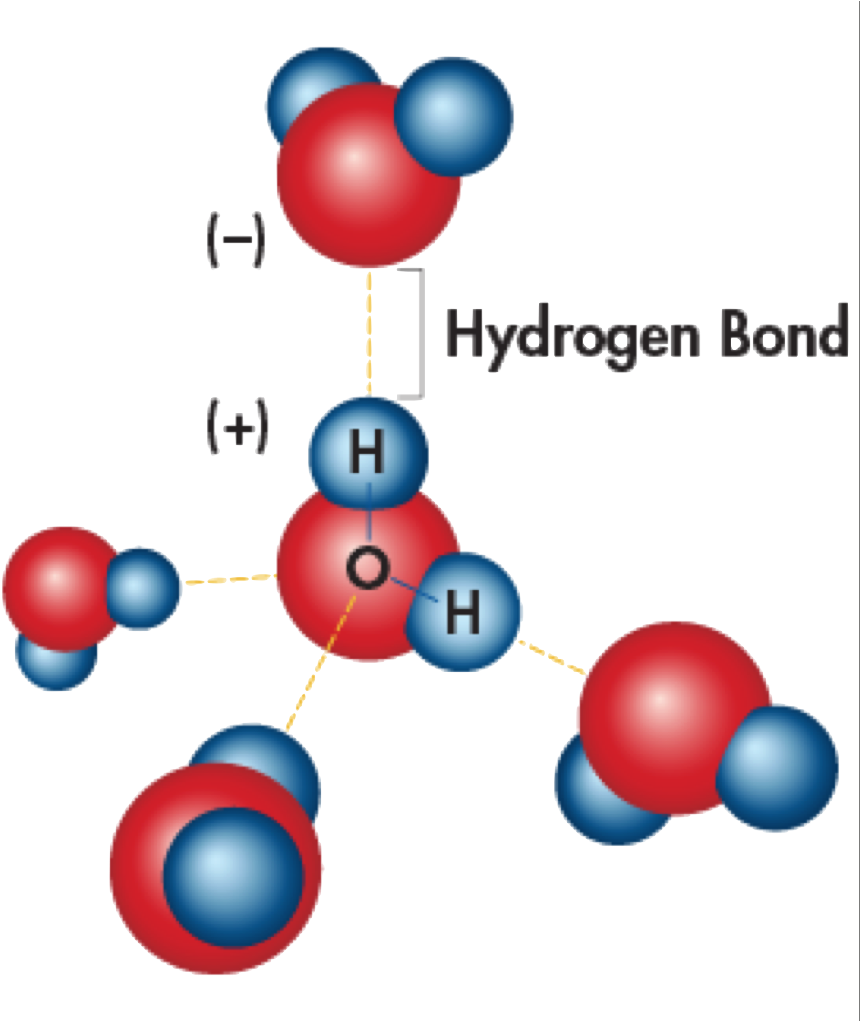
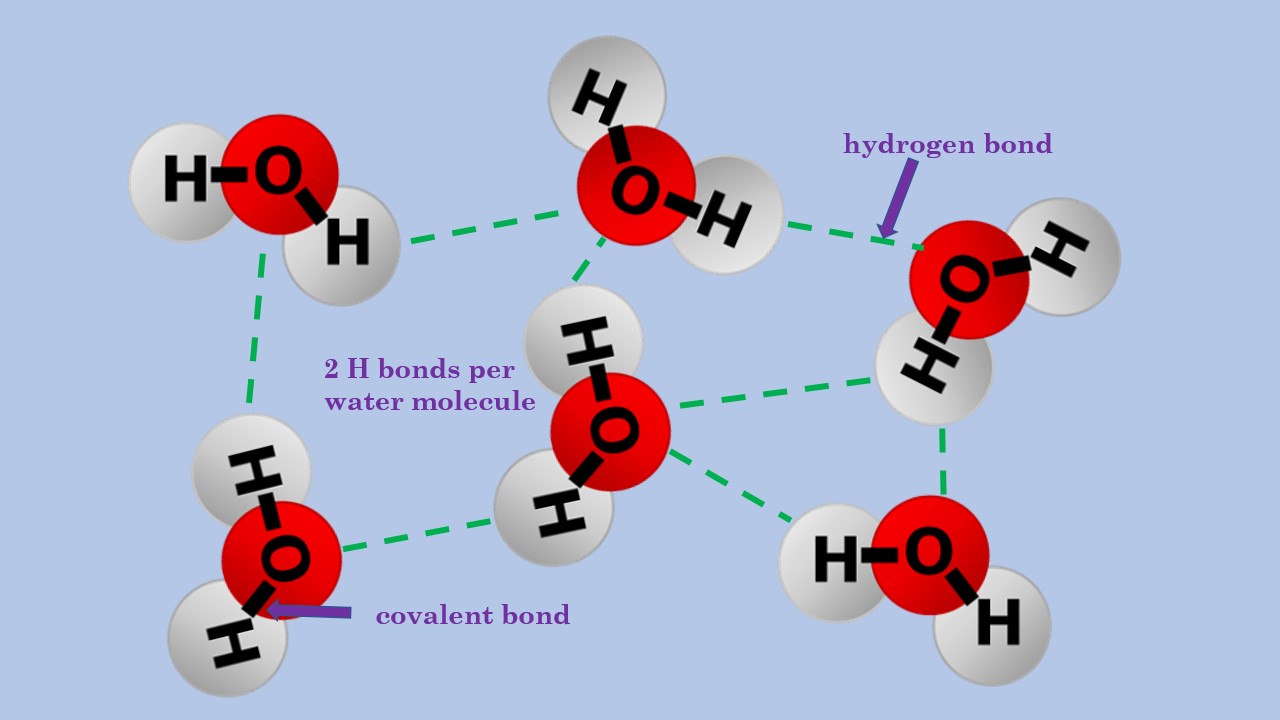
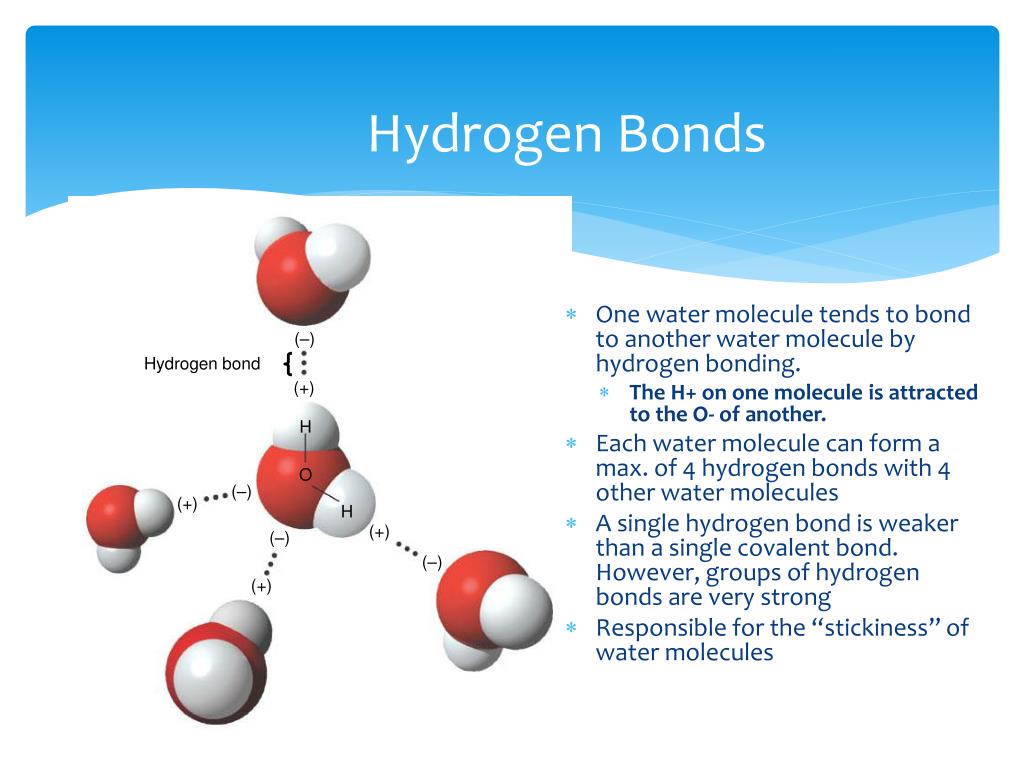
Bonds Form When Water Is Removed To Hold - In the case of water, hydrogen bonds form between neighboring hydrogen and oxygen atoms of adjacent water molecules. Peptide bonds form when water is removed to hold amino acids together. A drop of falling water is a group of water molecules held together by the hydrogen bonds between the molecules. What is the effect of excess heat or temperature on an enzyme? Peptide bonds are covalent bonds that link amino acids. The hydrogen bonds that form between water molecules account for some of the essential — and unique — properties of water. In water, each hydrogen nucleus is covalently bound to the central oxygen atom by a pair of electrons that are shared between them.
A drop of falling water is a group of water molecules held together by the hydrogen bonds between the molecules. Peptide bonds form when water is removed to hold amino acids together. In water, each hydrogen nucleus is covalently bound to the central oxygen atom by a pair of electrons that are shared between them. In the case of water, hydrogen bonds form between neighboring hydrogen and oxygen atoms of adjacent water molecules. The hydrogen bonds that form between water molecules account for some of the essential — and unique — properties of water. What is the effect of excess heat or temperature on an enzyme? Peptide bonds are covalent bonds that link amino acids.
The hydrogen bonds that form between water molecules account for some of the essential — and unique — properties of water. In the case of water, hydrogen bonds form between neighboring hydrogen and oxygen atoms of adjacent water molecules. Peptide bonds are covalent bonds that link amino acids. What is the effect of excess heat or temperature on an enzyme? A drop of falling water is a group of water molecules held together by the hydrogen bonds between the molecules. In water, each hydrogen nucleus is covalently bound to the central oxygen atom by a pair of electrons that are shared between them. Peptide bonds form when water is removed to hold amino acids together.
Primary and Secondary Bonds Owlcation
What is the effect of excess heat or temperature on an enzyme? A drop of falling water is a group of water molecules held together by the hydrogen bonds between the molecules. Peptide bonds are covalent bonds that link amino acids. Peptide bonds form when water is removed to hold amino acids together. The hydrogen bonds that form between water.
[Solved] Label the bonds and components of this water molecule
In the case of water, hydrogen bonds form between neighboring hydrogen and oxygen atoms of adjacent water molecules. Peptide bonds form when water is removed to hold amino acids together. The hydrogen bonds that form between water molecules account for some of the essential — and unique — properties of water. What is the effect of excess heat or temperature.
Bond energy
In the case of water, hydrogen bonds form between neighboring hydrogen and oxygen atoms of adjacent water molecules. A drop of falling water is a group of water molecules held together by the hydrogen bonds between the molecules. The hydrogen bonds that form between water molecules account for some of the essential — and unique — properties of water. Peptide.
Covalent bonding
What is the effect of excess heat or temperature on an enzyme? The hydrogen bonds that form between water molecules account for some of the essential — and unique — properties of water. In the case of water, hydrogen bonds form between neighboring hydrogen and oxygen atoms of adjacent water molecules. A drop of falling water is a group of.
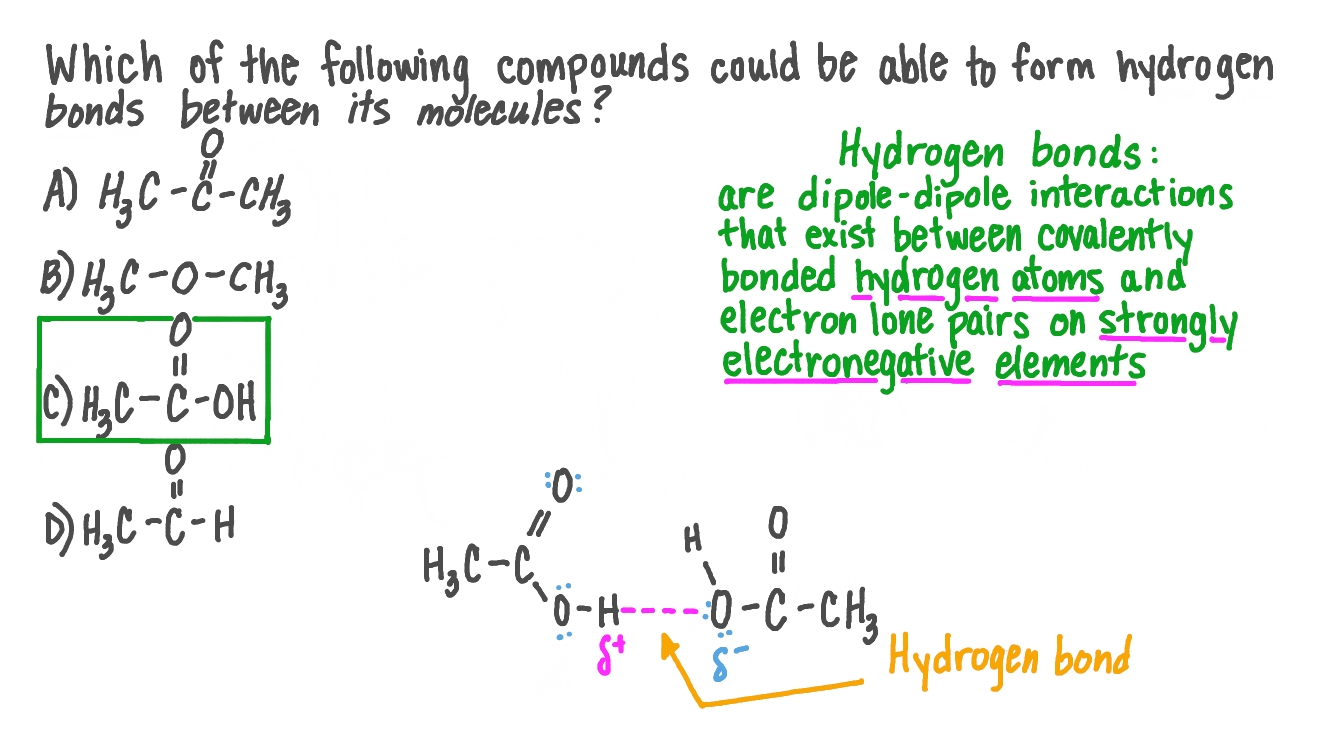
Question Video Identifying Which Compound Could Form Hydrogen Bonds
In the case of water, hydrogen bonds form between neighboring hydrogen and oxygen atoms of adjacent water molecules. In water, each hydrogen nucleus is covalently bound to the central oxygen atom by a pair of electrons that are shared between them. The hydrogen bonds that form between water molecules account for some of the essential — and unique — properties.
Download Hydrogen Bonding Is The Effect Of Water Molecules Attracted
What is the effect of excess heat or temperature on an enzyme? A drop of falling water is a group of water molecules held together by the hydrogen bonds between the molecules. Peptide bonds are covalent bonds that link amino acids. The hydrogen bonds that form between water molecules account for some of the essential — and unique — properties.
Hydrogen Bonding in water Dr. M. Chemistry Tutor
Peptide bonds form when water is removed to hold amino acids together. In water, each hydrogen nucleus is covalently bound to the central oxygen atom by a pair of electrons that are shared between them. Peptide bonds are covalent bonds that link amino acids. In the case of water, hydrogen bonds form between neighboring hydrogen and oxygen atoms of adjacent.
PPT Properties of Water PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
A drop of falling water is a group of water molecules held together by the hydrogen bonds between the molecules. Peptide bonds are covalent bonds that link amino acids. The hydrogen bonds that form between water molecules account for some of the essential — and unique — properties of water. In water, each hydrogen nucleus is covalently bound to the.
The diagram shows hydrogen bonds between water molecules. Label the
In water, each hydrogen nucleus is covalently bound to the central oxygen atom by a pair of electrons that are shared between them. In the case of water, hydrogen bonds form between neighboring hydrogen and oxygen atoms of adjacent water molecules. The hydrogen bonds that form between water molecules account for some of the essential — and unique — properties.
Biomolecules flashcards 1 How do hydrogen bonds form between water
The hydrogen bonds that form between water molecules account for some of the essential — and unique — properties of water. In the case of water, hydrogen bonds form between neighboring hydrogen and oxygen atoms of adjacent water molecules. In water, each hydrogen nucleus is covalently bound to the central oxygen atom by a pair of electrons that are shared.
Peptide Bonds Are Covalent Bonds That Link Amino Acids.
A drop of falling water is a group of water molecules held together by the hydrogen bonds between the molecules. In the case of water, hydrogen bonds form between neighboring hydrogen and oxygen atoms of adjacent water molecules. Peptide bonds form when water is removed to hold amino acids together. The hydrogen bonds that form between water molecules account for some of the essential — and unique — properties of water.
What Is The Effect Of Excess Heat Or Temperature On An Enzyme?
In water, each hydrogen nucleus is covalently bound to the central oxygen atom by a pair of electrons that are shared between them.