B Sheet Structure - Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains. The primary structure of a protein is simply the amino acid sequence. The side chains in the beta sheet are normal to the plane of the sheet, extending out from the plane on alternating sides. The secondary structure of a protein describes how segments. The secondary structure of proteins comprises organized regions of polypeptide backbone stabilized by hydrogen bonds.
The side chains in the beta sheet are normal to the plane of the sheet, extending out from the plane on alternating sides. The secondary structure of a protein describes how segments. The primary structure of a protein is simply the amino acid sequence. Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains. The secondary structure of proteins comprises organized regions of polypeptide backbone stabilized by hydrogen bonds.
Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains. The primary structure of a protein is simply the amino acid sequence. The secondary structure of a protein describes how segments. The side chains in the beta sheet are normal to the plane of the sheet, extending out from the plane on alternating sides. The secondary structure of proteins comprises organized regions of polypeptide backbone stabilized by hydrogen bonds.
(A) Chemical structures of the three βsheet forming peptides used in
The side chains in the beta sheet are normal to the plane of the sheet, extending out from the plane on alternating sides. The primary structure of a protein is simply the amino acid sequence. The secondary structure of proteins comprises organized regions of polypeptide backbone stabilized by hydrogen bonds. The secondary structure of a protein describes how segments. Protein.
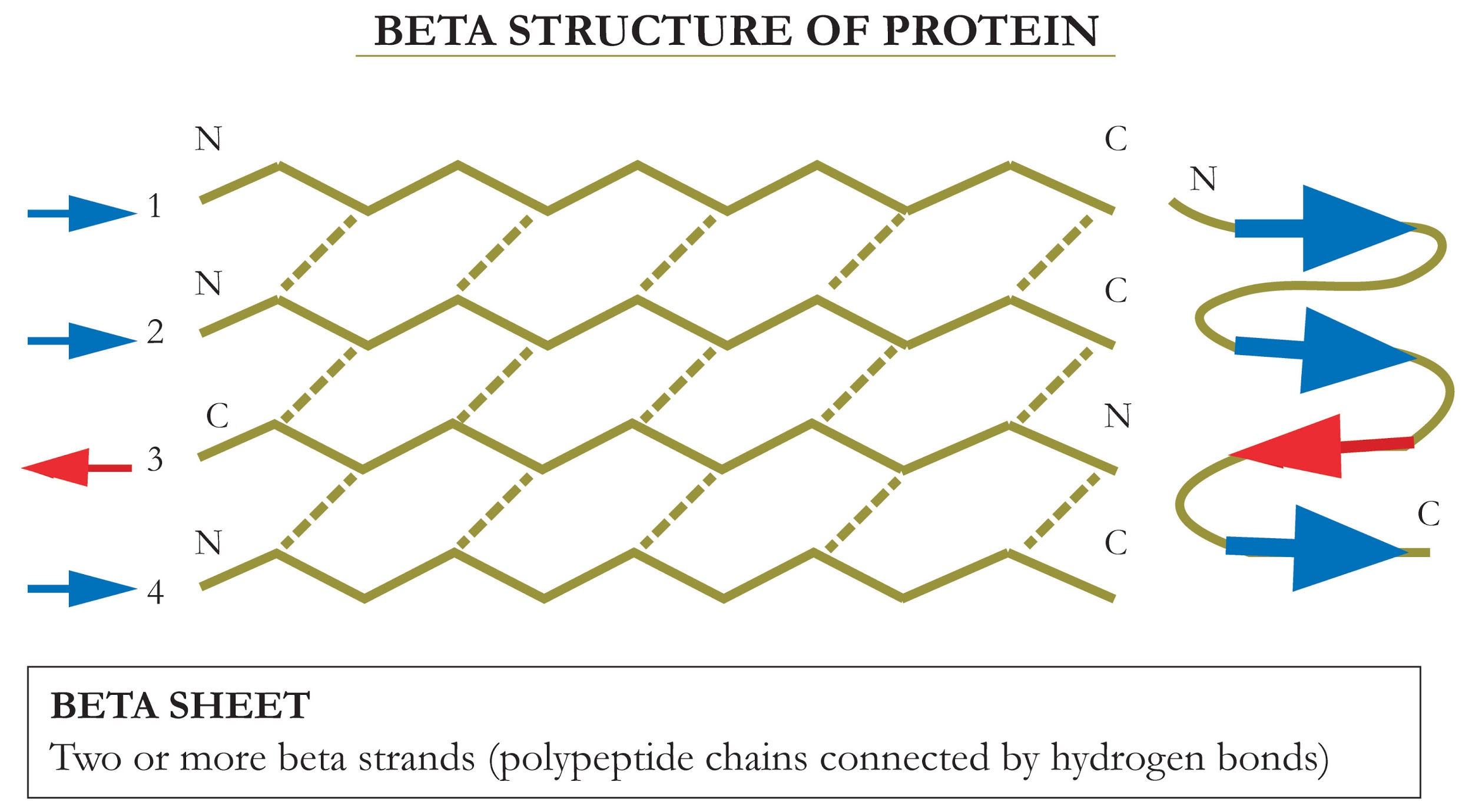
Biochemistry Fundamentals Secondary Structure 2 The Beta Sheet
The primary structure of a protein is simply the amino acid sequence. The secondary structure of a protein describes how segments. Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains. The side chains in the beta sheet are normal to the plane of the sheet, extending out from the plane on alternating sides..
What Is A Beta Sheet
The secondary structure of a protein describes how segments. The primary structure of a protein is simply the amino acid sequence. The side chains in the beta sheet are normal to the plane of the sheet, extending out from the plane on alternating sides. Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains..
Biochemistry Glossary Protein Structure Class 2(b). Secondary Beta
Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains. The primary structure of a protein is simply the amino acid sequence. The secondary structure of proteins comprises organized regions of polypeptide backbone stabilized by hydrogen bonds. The side chains in the beta sheet are normal to the plane of the sheet, extending out.
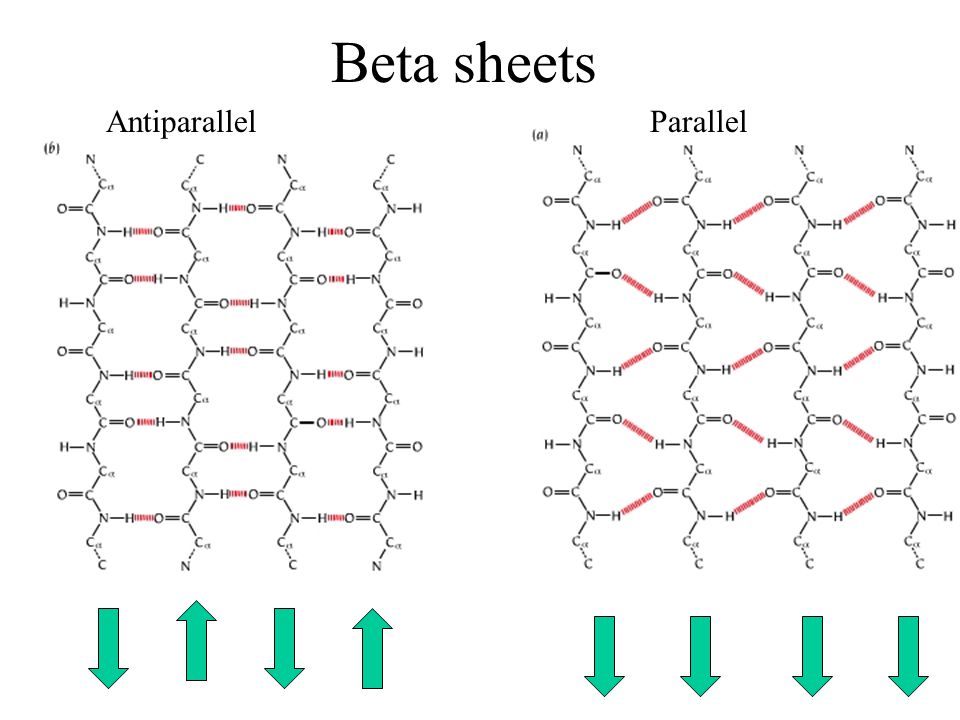
Beta Sheet Antiparallel Vs Parallel
The side chains in the beta sheet are normal to the plane of the sheet, extending out from the plane on alternating sides. The secondary structure of proteins comprises organized regions of polypeptide backbone stabilized by hydrogen bonds. Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains. The primary structure of a protein.
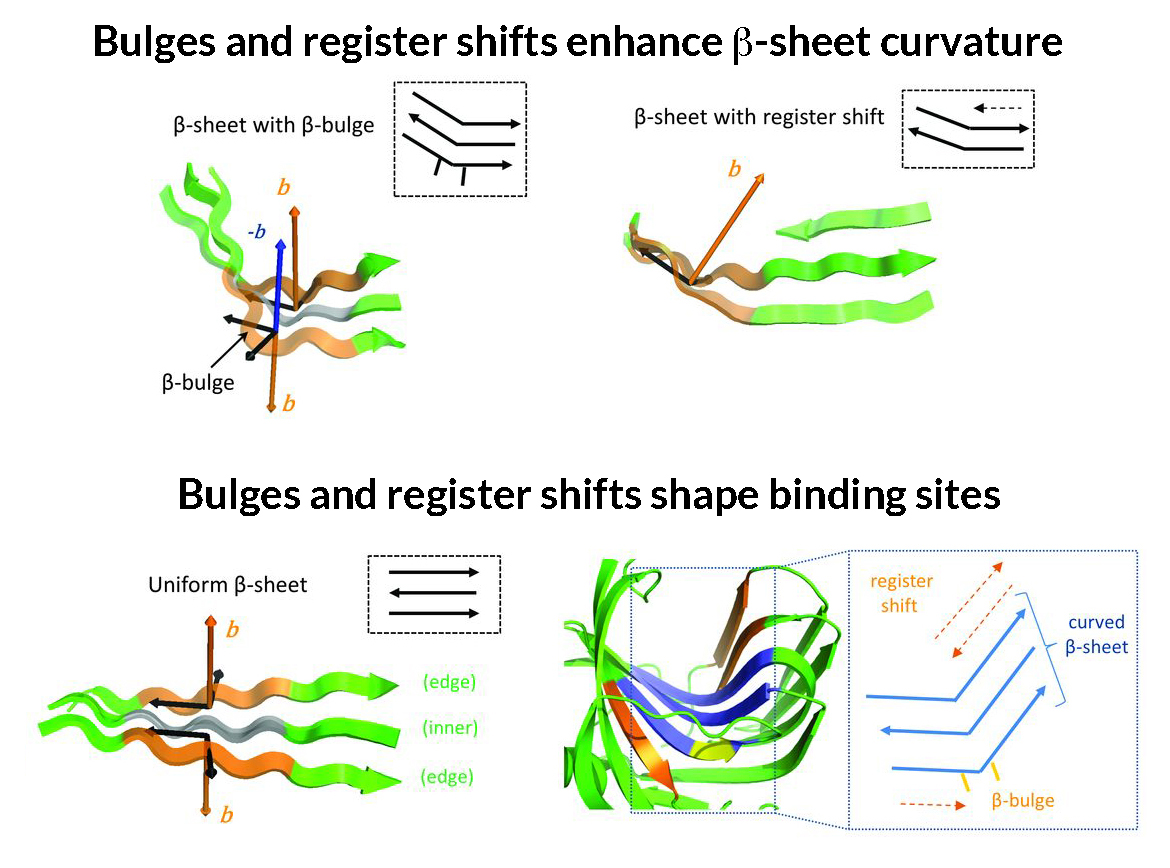
Bending the (βSheet) Curve to Shape Protein Cavities
The secondary structure of a protein describes how segments. The primary structure of a protein is simply the amino acid sequence. The secondary structure of proteins comprises organized regions of polypeptide backbone stabilized by hydrogen bonds. Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains. The side chains in the beta sheet are.
Infinite Pleated βsheet Formed By The βhairpin, 58 OFF
Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains. The secondary structure of a protein describes how segments. The side chains in the beta sheet are normal to the plane of the sheet, extending out from the plane on alternating sides. The secondary structure of proteins comprises organized regions of polypeptide backbone stabilized.
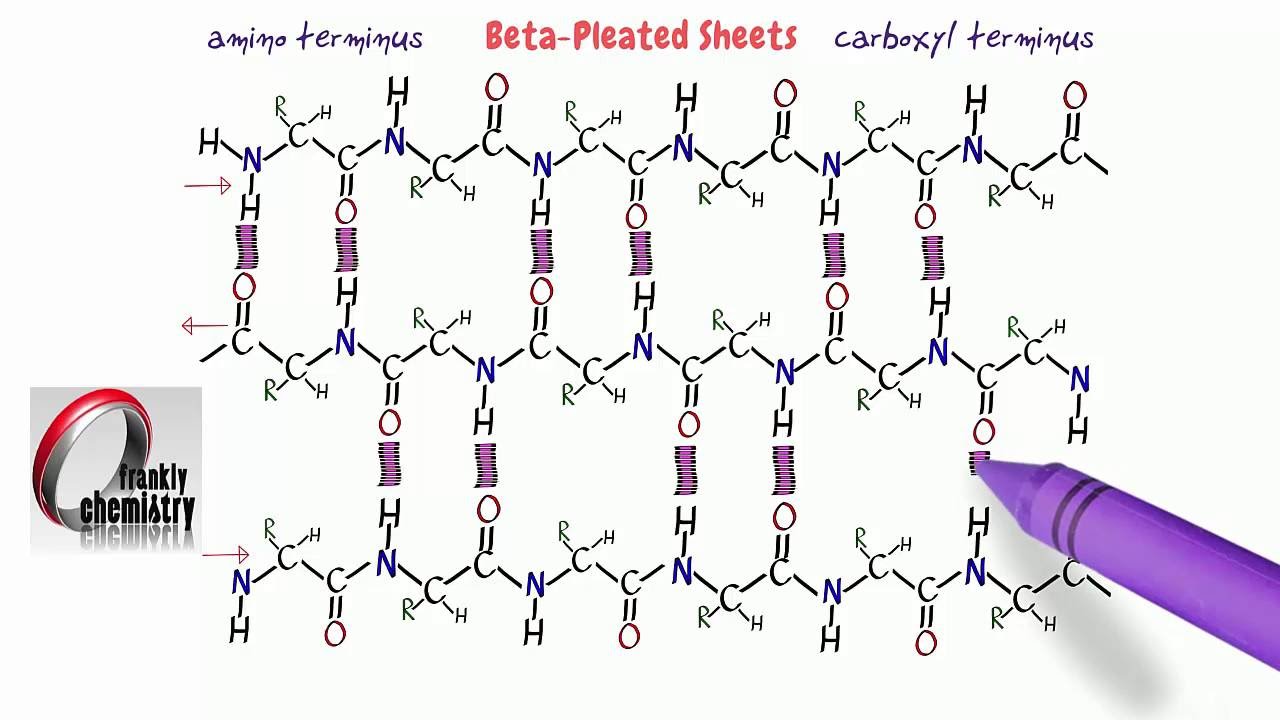
Beta pleated sheet Secondary structure of protein YouTube
The secondary structure of proteins comprises organized regions of polypeptide backbone stabilized by hydrogen bonds. Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains. The side chains in the beta sheet are normal to the plane of the sheet, extending out from the plane on alternating sides. The primary structure of a protein.
Amino Acids 8. The betapleated sheets secondary structure of Proteins
The secondary structure of a protein describes how segments. The primary structure of a protein is simply the amino acid sequence. The side chains in the beta sheet are normal to the plane of the sheet, extending out from the plane on alternating sides. Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains..
Secondary structures of keratin protein (beta pleated sheets and alpha
The secondary structure of a protein describes how segments. The primary structure of a protein is simply the amino acid sequence. The secondary structure of proteins comprises organized regions of polypeptide backbone stabilized by hydrogen bonds. Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains. The side chains in the beta sheet are.
The Primary Structure Of A Protein Is Simply The Amino Acid Sequence.
The side chains in the beta sheet are normal to the plane of the sheet, extending out from the plane on alternating sides. Protein secondary structure is the local spatial conformation of the polypeptide backbone excluding the side chains. The secondary structure of proteins comprises organized regions of polypeptide backbone stabilized by hydrogen bonds. The secondary structure of a protein describes how segments.