Axiom Math Definition - An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be proven. It is accepted as true, without proof, as the basis for argument. An axiom serves as the base. Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in mathematics.
An axiom serves as the base. It is accepted as true, without proof, as the basis for argument. Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in mathematics. An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be proven.
An axiom serves as the base. Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in mathematics. It is accepted as true, without proof, as the basis for argument. An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be proven.
What is an axiom?
It is accepted as true, without proof, as the basis for argument. An axiom serves as the base. An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be proven. Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in.
Physics; formulated so as to be indubitable and thus forming a final
It is accepted as true, without proof, as the basis for argument. Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in mathematics. An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be proven. An axiom serves as the.
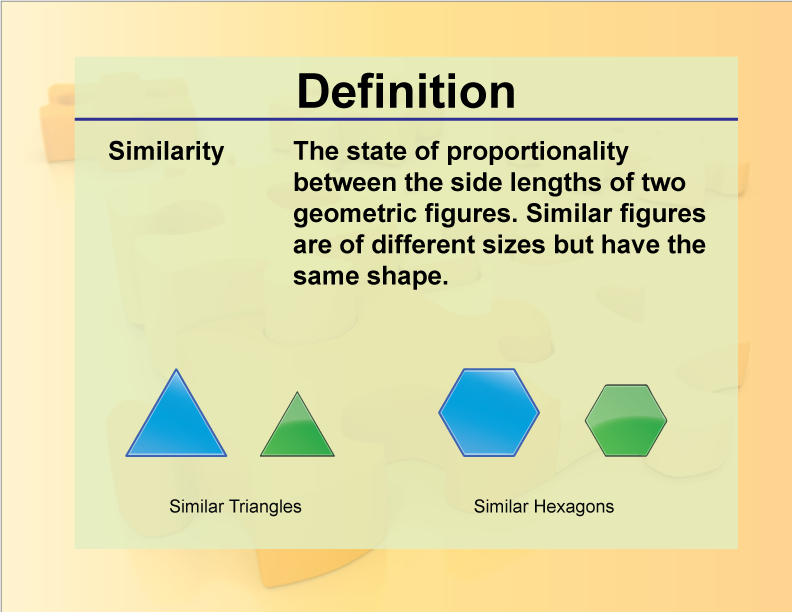
DefinitionGeometry BasicsSimilarity Media4Math
It is accepted as true, without proof, as the basis for argument. An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be proven. Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in mathematics. An axiom serves as the.
Definition of Axiom YouTube
An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be proven. An axiom serves as the base. Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in mathematics. It is accepted as true, without proof, as the basis for.
Discrete Mathematics Chapter 1 Logic and proofs 1282020
Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in mathematics. An axiom serves as the base. It is accepted as true, without proof, as the basis for argument. An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be.
PPT Axiomatic Systems PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4520354
It is accepted as true, without proof, as the basis for argument. Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in mathematics. An axiom serves as the base. An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be.
What Are Axioms? YouTube
Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in mathematics. An axiom serves as the base. It is accepted as true, without proof, as the basis for argument. An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be.
What is an Axiom Definition of Axiom
An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be proven. Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in mathematics. It is accepted as true, without proof, as the basis for argument. An axiom serves as the.
What is an axiom?
An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be proven. Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in mathematics. An axiom serves as the base. It is accepted as true, without proof, as the basis for.
Solved What axiom can justify this statement 9* (8+5)=(9* 8)+(9* 5
It is accepted as true, without proof, as the basis for argument. An axiom serves as the base. Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in mathematics. An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be.
It Is Accepted As True, Without Proof, As The Basis For Argument.
Axioms or postulate is defined as a statement that is accepted as true and correct, called as a theorem in mathematics. An axiom serves as the base. An axiom is a statement that is true or assumed to be true without any proof whereas a theorem must be proven.